Obstetrical outcome and treatments in seronegative primary APS: data from European retrospective study
- PMID: 32848089
- PMCID: PMC7507995
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001340
Obstetrical outcome and treatments in seronegative primary APS: data from European retrospective study
Abstract
Objective: To compare characteristics, pregnancies and treatments during pregnancies of seronegative and seropositive antiphospholipid syndrome (APS), to analyse factors associated with obstetrical outcome.
Patients and methods: Inclusion criteria were: (1) thrombotic and/or obstetrical APS (Sydney criteria); (2) absence of conventional antiphospholipid antibodies (APL); (3) at least one persistent non-conventional APL among IgA anticardiolipin antibodies, IgA anti-B2GPI, anti-vimentin G/M, anti-annexin V G/M, anti-phosphatidylethanolamine G/M and anti-phosphatidylserine/prothrombin G/M antibodies. The exclusion criteria were: (1) systemic lupus erythematosus ( SLE) or SLE-like disease; and (2) other connective tissue disease.
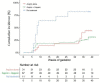
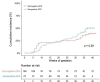
Results: A total of 187 women (mean 33±5 years) with seronegative APS were included from 14 centres in Austria, Spain, Italy, Slovenia and France and compared with 285 patients with seropositive APS. Seronegative APS has more obstetrical rather than thrombotic phenotypes, with only 6% of venous thrombosis in comparison to seropositive APS. Cumulative incidence of adverse obstetrical events was similar in seronegative and seropositive APS patients, although higher rates of intrauterine deaths (15% vs 5%; p=0.03), of preeclampsia (7% vs 16%, p=0.048) and lower live birth term (36±3 vs 38±3 weeks of gestation; p=0.04) were noted in seropositive APS. The cumulative incidence of adverse obstetrical events was significantly improved in treated versus untreated seronegative APS (log rank<0.05), whereas there was no difference between patients who received aspirin or aspirin-low-molecular weighted heparin combination.
Conclusion: Several non-criteria APL can be detected in patients with clinical APS features without any conventional APL, with various rates. The detection of non-criteria APL and thus the diagnosis of seronegative APS could discuss the therapeutic management similar to seropositive APS, but well-designed controlled studies are necessary.
Keywords: Antibodies; Antiphospholipid; Antiphospholipid Syndrome; Health Care; Outcome and Process Assessment.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Non-conventional antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with clinical obstetrical APS: Prevalence and treatment efficacy in pregnancies.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016 Oct;46(2):232-237. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2016.05.006. Epub 2016 May 25. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2016. PMID: 27432776
-
The value of IgA antiphospholipid testing for diagnosis of antiphospholipid (Hughes) syndrome in systemic lupus erythematosus.J Rheumatol. 2001 Dec;28(12):2637-43. J Rheumatol. 2001. PMID: 11764209
-
Refractory obstetrical antiphospholipid syndrome: Features, treatment and outcome in a European multicenter retrospective study.Autoimmun Rev. 2017 Jul;16(7):730-734. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.05.006. Epub 2017 May 4. Autoimmun Rev. 2017. PMID: 28478081 Review.
-
'Non-criteria antiphospholipid antibodies': bridging the gap between seropositive and seronegative antiphospholipid syndrome.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022 Feb 2;61(2):826-833. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keab414. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2022. PMID: 33970223
-
Seronegative antiphospholipid syndrome: refining the value of "non-criteria" antibodies for diagnosis and clinical management.Haematologica. 2020 Mar;105(3):562-572. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.221945. Epub 2020 Jan 30. Haematologica. 2020. PMID: 32001534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Phosphatidylserine/Prothrombin Antibodies in Healthy Women with Unexplained Recurrent Pregnancy Loss.J Clin Med. 2021 May 13;10(10):2094. doi: 10.3390/jcm10102094. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34068095 Free PMC article.
-
Hydroxychloroquine in recurrent pregnancy loss: data from a French prospective multicenter registry.Hum Reprod. 2024 Sep 1;39(9):1934-1941. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deae146. Hum Reprod. 2024. PMID: 38942601 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody profiles in the mosaic of 'seronegative' APS syndrome.Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Nov 12;218(3):275-282. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxae079. Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39192704 Free PMC article.
-
A case of repeated in-stent restenosis of coronary artery as a primary manifestation of seronegative antiphospholipid antibody syndrome.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jan 6;24(1):32. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03568-2. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38184550 Free PMC article.
-
Non-Criteria Obstetric Antiphospholipid Syndrome: How Different Is from Sidney Criteria? A Single-Center Study.Biomedicines. 2022 Nov 15;10(11):2938. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112938. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36428506 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
