Susceptibility of virulent and resistant Escherichia coli strains to non-polar and polar compounds identified in Microplumeria anomala
- PMID: 32848314
- PMCID: PMC7429380
- DOI: 10.14202/vetworld.2020.1376-1387
Susceptibility of virulent and resistant Escherichia coli strains to non-polar and polar compounds identified in Microplumeria anomala
Abstract
Background and aim: Escherichia coli is one of the main pathogens responsible for veterinary and human infections, and it is associated with significant economic losses in the livestock, as it causes severe diseases to humans, particularly in children. For that reason, there is a need for introducing new drugs to treat E. coli diseases. The Brazilian species richness is a source of potential new antibacterial natural products. The study aimed at the biological and chemical investigation of the organic extract obtained from the stem of Microplumeria anomala (Apocynaceae), EB127, as it was identified as a potential source of new antibacterial compounds to be used in Veterinary.
Materials and methods: The antibacterial activity was evaluated by disk diffusion and microdilution assays; chromatography, nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometry, and mass spectrometry were used in the isolation and identification of compounds.
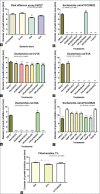
Results: EB127 showed activity against E. coli ATCC25922, and against three E. coli strains that were isolated from frigarte's cloaca, named 31/1A, 35A, and 51A. Lupeol, 3-acetyl-11-oxo-β-amyrin, 3-acetyl-11-oxo-α-amyrin, sitosterol, stigmasterol, 3β,7α-dihydroxy-cholest-5-ene, 3β-hydroxy-cholest-5-en-7-one, and 3β-hydroxy-cholest-5,22-dien-7-one were identified in fraction Hex/CHCl3, while loganin, loganic acid, methylanomaline, and anomaline were all identified in EB127 and protocatechuic acid hexoside, ferulic acid, secoxyloganin, feruloylquinic acid, vanillic acid hexoside, protocatechuic acid-4-O-β-hexoside, and rosmarinic acid were tentatively identified in fraction 10%ACN/H2O. E. coli 51A (virulent/non-resistant) showed sensitivity to the antibacterial action of fraction Hex/CHCl3 which contains alkaloids, triterpenes, and steroids, while E. coli 35A (resistant/non-virulent) were more susceptible to 10%ACN/H2O, which contains iridoids as loganin and loganic acid, and glycosylated and non-glycosylated caffeic acids.
Conclusion: Fraction 10%ACN/H2O is of interest in pursuing new drugs to treat resistant E. coli, in veterinary. All compounds were isolated from the plant for the first time and have shown potential as new antibacterial natural products from Amazon plants to be used in veterinary and human diseases.
Keywords: antibacterial agents; companion animals; livestock; plant extracts; poultry; tropical rainforest.
Copyright: © Camargo, et al.
Figures


References
-
- Radostitis O.M, Gay C, Blood D.C, Hinchcliff K.W, Constable P.D. Veterinary Medicine a Textbook of the Diseases of Cattle Horses Sheep Pigs and Goats. 11th ed. Philadelphia: Saunders; 2017. p. 2278.
-
- Machado L.S, Nascimento E.R, Pereira A.L.A, Almeida D.O, Abreu D.L.C, Gouvêa R. PCR na detecção de gene Fel Ade Escherichia coliem frangos de corte condenados por aerossaculite pela Inspeção Sanitária Federal. Arq. Inst. Biol. 2013;80(2):145–149.
-
- Hagman R. Pyometra in small animals. Vet. Clin. North Am. Small Anim. Pract. 2018;48(4):639–661. - PubMed
-
- Scholar E.M, Pratt W.B. the Antimicrobial Drugs. oxford University Press, Oxford. 2000
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
