Atorvastatin Combined with Low-Dose Dexamethasone Treatment Protects Endothelial Function Impaired by Chronic Subdural Hematoma via the Transcription Factor KLF-2
- PMID: 32848367
- PMCID: PMC7429211
- DOI: 10.2147/DDDT.S256050
Atorvastatin Combined with Low-Dose Dexamethasone Treatment Protects Endothelial Function Impaired by Chronic Subdural Hematoma via the Transcription Factor KLF-2
Abstract
Objective: Our previous study showed that the combination therapy with atorvastatin and low-dose dexamethasone protected endothelial cell function in chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH) injury. In this study, we aimed to investigate the mechanism underlying the effects of this combination therapy on CSDH-induced cell dysfunction.
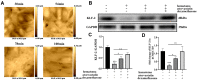
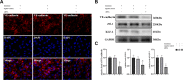
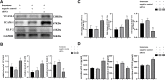
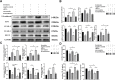
Methods: Monocytes and endothelial cells were cocultured with CSDH patient hematoma samples to mimic the pathological microenvironment of CSDH. Monocytes (THP-1 cells) and endothelial cells (hCMEC/D3 cells) were cocultured in a transwell system for 24 h before stimulation with hematoma samples diluted in endothelial cell medium (ECM) at a 1:1 ratio. Tight junction markers were detected by Western blotting, PCR and immunofluorescence. hCMEC/D3 cells were collected for Western blot and PCR analyses to detect changes in the expression levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM-1), intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM-1), and Kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF-2). The IL-6, IL-10 and VEGF levels in the supernatant were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results: KLF-2 expression in endothelial cells was decreased after stimulation with CSDH patient hematoma samples, but combination therapy with atorvastatin and low-dose dexamethasone reversed this trend. KLF-2 protected injured cells by increasing the expression of VE-cadherin and ZO-1; attenuating the expression of VCAM-1, ICAM-1, IL-6 and VEGF; and enhancing the expression of IL-10, all of which play pivotal roles in endothelial inflammation. Moreover, the effect of combination therapy with atorvastatin and low-dose dexamethasone was obviously reduced in endothelial cells with KLF-2 knockdown compared with normal cells.
Conclusion: Coculture with hematoma samples decreased KLF-2 expression in human cerebral endothelial cells. Combination therapy with atorvastatin and low-dose dexamethasone counteracted hematoma-induced KLF-2 suppression in human cerebral endothelial cells to attenuate robust endothelial inflammation and permeability. KLF-2 plays an important role in drug therapy for CSDH and may become the key factor in treatment and prognosis.
Keywords: Kruppel-like factor 2; atorvastatin combined with low-dose dexamethasone treatment; chronic subdural hematoma; endothelial inflammation and permeability.
© 2020 Fan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest and report no conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures
References
-
- Allison A, Edlmann E, Kolias AG, et al. Statistical analysis plan for the Dex-CSDH trial: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a 2-week course of dexamethasone for adult patients with a symptomatic chronic subdural haematoma. Trials. 2019;20(1):698. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3866-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

