Supramolecular Vesicles Based on Amphiphilic Pillar[n]arenes for Smart Nano-Drug Delivery
- PMID: 32848395
- PMCID: PMC7429218
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S255637
Supramolecular Vesicles Based on Amphiphilic Pillar[n]arenes for Smart Nano-Drug Delivery
Abstract
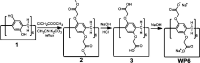
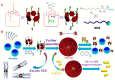
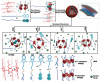
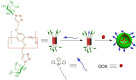
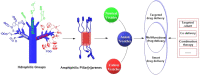
Supramolecular vesicles are the most popular smart nano-drug delivery systems (SDDs) because of their unique cavities, which have high loading carrying capacity and controlled-release action in response to specific stimuli. These vesicles are constructed from amphiphilic molecules via host-guest complexation, typically with targeted stimuli-responsive units, which are particularly important in biotechnology and biomedicine applications. Amphiphilic pillar[n]arenes, which are novel and functional macrocyclic host molecules, have been widely used to construct supramolecular vesicles because of their intrinsic rigid and symmetrical structure, electron-rich cavities and excellent properties. In this review, we first explain the synthesis of three types of amphiphilic pillar[n]arenes: neutral, anionic and cationic pillar[n]arenes. Second, we examine supramolecular vesicles composed of amphiphilic pillar[n]arenes recently used for the construction of SDDs. In addition, we describe the prospects for multifunctional amphiphilic pillar[n]arenes, particularly their potential in novel applications.
Keywords: amphiphilic pillar[n]arenes; drug delivery; smart; supramolecular vesicles.
© 2020 Hua et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures















Similar articles
-
Stimuli-Responsive Amphiphilic Pillar[n]arene Nanovesicles for Targeted Delivery of Cancer Drugs.ACS Omega. 2021 Sep 30;6(40):25876-25883. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04297. eCollection 2021 Oct 12. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34660950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in pillar[n]arenes: synthesis and applications based on host-guest interactions.Chem Commun (Camb). 2016 Jul 19;52(60):9316-26. doi: 10.1039/c6cc03641d. Chem Commun (Camb). 2016. PMID: 27332040 Review.
-
Supramolecular Drug Delivery Systems Based on Water-Soluble Pillar[n]arenes.Chem Rec. 2016 Jun;16(3):1216-27. doi: 10.1002/tcr.201500265. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Chem Rec. 2016. PMID: 27061964
-
Stimuli-responsive supramolecular nano-systems based on pillar[n]arenes and their related applications.J Mater Chem B. 2019 Dec 11;7(48):7656-7675. doi: 10.1039/c9tb01913h. J Mater Chem B. 2019. PMID: 31746931 Review.
-
Stimuli-Responsive Supramolecular Assemblies Constructed from Pillar[ n]arenes.Acc Chem Res. 2018 Jul 17;51(7):1656-1666. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.8b00157. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Acc Chem Res. 2018. PMID: 29889488
Cited by
-
Dendrimer-based drug delivery systems: history, challenges, and latest developments.J Biol Eng. 2022 Jul 25;16(1):18. doi: 10.1186/s13036-022-00298-5. J Biol Eng. 2022. PMID: 35879774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Sensing with Host Systems for Hyperpolarized 129Xe.Molecules. 2020 Oct 11;25(20):4627. doi: 10.3390/molecules25204627. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33050669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Stimuli-Responsive Amphiphilic Pillar[n]arene Nanovesicles for Targeted Delivery of Cancer Drugs.ACS Omega. 2021 Sep 30;6(40):25876-25883. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c04297. eCollection 2021 Oct 12. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34660950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Structure to Function: The Promise of PAMAM Dendrimers in Biomedical Applications.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jul 18;17(7):927. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17070927. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40733135 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1-[1,4-Bis(but-3-en-1-yl-oxy)]-2,3,4,5-(1,4-dimeth-oxy)pillar[5]arene-1,4-di-bromo-butane 1:1 inclusion complex.IUCrdata. 2023 Jul 14;8(Pt 7):x230588. doi: 10.1107/S2414314623005886. eCollection 2023 Jul. IUCrdata. 2023. PMID: 37937131 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

