Effectiveness of Exercise Therapy on Gait Function in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 32848436
- PMCID: PMC7425100
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S261175
Effectiveness of Exercise Therapy on Gait Function in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Patients: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
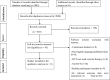
The purpose of this study was to review the current evidence on the effectiveness of exercise therapy on gait function in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. A comprehensive search of literature published between October 2010 and May 2020 was conducted using the following electronic databases; PubMed, AMED, CINAHL, ScienceDirect, Cochrane Library, PEDro and Google Scholar. Randomized control trials conducted to determine the effectiveness of exercise therapy on gait function in patients with diabetic neuropathy were included in this review. Non-English language published papers were excluded. This review was done in compliance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. Data extraction and risk of bias assessment of the studies were carried out independently by two authors. The methodological quality of the studies was evaluated using the PEDro scale and GRADE approach. The overall methodological quality of studies rated from moderate to high. Meta-analysis was not carried out due to the heterogeneity of included trials. The primary outcome measures of gait functions were the six-minute walk test, 10-meter walk test and Tinetti scale. Nine randomized controlled trials with 370 participants were analyzed. Out of them, eight studies proved its effectiveness on gait function on individuals with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. The finding of this study suggested that multi-component exercise therapy consisted of strength, ROM exercise, balance, flexibility and stretching exercises, circuit exercise training, and gait training found to enhance gait function for individuals suffering with diabetic peripheral neuropathy compared to control groups.
Keywords: diabetic pain; exercise therapy; functional training; gait; peripheral neuropathy; systematic review.
© 2020 Melese et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Long-Term Effects of Whole-Body Vibration on Human Gait: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Neurol. 2019 Jun 19;10:627. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00627. eCollection 2019. Front Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31316447 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum.Mult Scler. 2016 Oct;22(12):NP9-NP11. doi: 10.1177/1352458515585718. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Mult Scler. 2016. PMID: 26041800
-
Exercise and Neuropathy: Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis.Sports Med. 2022 May;52(5):1043-1065. doi: 10.1007/s40279-021-01596-6. Epub 2021 Dec 29. Sports Med. 2022. PMID: 34964950
-
Effectiveness of exercise interventions on physical function in community-dwelling frail older people: an umbrella review of systematic reviews.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018 Mar;16(3):752-775. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2017-003551. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2018. PMID: 29521871
-
Effectiveness of Action Observation Training on Upper Limb Motor Function in Children with Hemiplegic Cerebral Palsy: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.Pediatric Health Med Ther. 2020 Sep 15;11:335-346. doi: 10.2147/PHMT.S266720. eCollection 2020. Pediatric Health Med Ther. 2020. PMID: 32982541 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Balance, Gait, Functionality and Fall Occurrence in Adults and Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Associated Peripheral Neuropathy.Clin Pract. 2024 Sep 28;14(5):2044-2055. doi: 10.3390/clinpract14050161. Clin Pract. 2024. PMID: 39451876 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Risk Factors Responsible for Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Diabetic Foot During the COVID-19 Pandemic.Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2023 Jan 27;28(1):85-91. doi: 10.4103/ijnmr.ijnmr_180_21. eCollection 2023 Jan-Feb. Iran J Nurs Midwifery Res. 2023. PMID: 37250947 Free PMC article.
-
Foot-ankle therapeutic exercise program can improve gait speed in people with diabetic neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial.Sci Rep. 2022 May 9;12(1):7561. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-11745-0. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35534614 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of lower body positive pressure aerobic training on fall risk in patients with diabetic polyneuropathy: randomized controlled trial.Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022 Feb;58(1):33-42. doi: 10.23736/S1973-9087.21.06847-7. Epub 2021 Oct 12. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2022. PMID: 34636527 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: The Need for New Approaches.J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024 Jan;18(1):159-167. doi: 10.1177/19322968221132252. Epub 2022 Oct 28. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 36305521 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical