Role of Ginkgolides in the Inflammatory Immune Response of Neurological Diseases: A Review of Current Literatures
- PMID: 32848639
- PMCID: PMC7411855
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsys.2020.00045
Role of Ginkgolides in the Inflammatory Immune Response of Neurological Diseases: A Review of Current Literatures
Abstract
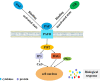
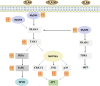
The inflammatory immune response (IIR) is a physiological or excessive systemic response, induced by inflammatory immune cells according to changes in the internal and external environments. An excessive IIR is the pathological basis for the generation and development of neurological diseases. Ginkgolides are one of the important medicinal ingredients in Ginkgo biloba. Many studies have verified that ginkgolides have anti-platelet-activating, anti-apoptotic, anti-oxidative, neurotrophic, and neuroimmunomodulatory effects. Inflammatory immunomodulation is mediated by inhibition of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathways. They also inhibit the platelet-activating factor (PAF)-mediated signal transduction to attenuate the inflammatory response. Herein, we reviewed the studies on the roles of ginkgolides in inflammatory immunomodulation and suggested its potential role in novel treatments for neurological diseases.
Keywords: Guillain–Barré syndrome; ginkgolides; inflammatory immune response; multiple sclerosis; neurological diseases.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Liu, Liu, Aerqin and Wu.
Figures

References
-
- Aicher A., Shu G. L., Magaletti D., Mulvania T., Pezzutto A., Craxton A., et al. (1999). Differential role for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in regulating CD40-induced gene expression in dendritic cells and B cells. J. Immunol. 163, 5786–5795. - PubMed
-
- Bastianetto S., Zheng W. H., Quirion R. (2000). The Ginkgo biloba extract (EGb 761) protects and rescues hippocampal cells against nitric oxide-induced toxicity: involvement of its flavonoid constituents and protein kinase C. J. Neurochem. 74, 2268–2277. 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2000.0742268.x - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

