H2S Donors Reverse Age-Related Gastric Malfunction Impaired Due to Fructose-Induced Injury via CBS, CSE, and TST Expression
- PMID: 32848752
- PMCID: PMC7396573
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.01134
H2S Donors Reverse Age-Related Gastric Malfunction Impaired Due to Fructose-Induced Injury via CBS, CSE, and TST Expression
Abstract
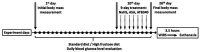
Objective: Excess of fructose consumption is related to life-treating conditions that affected more than a third of the global population. Therefore, to identify a newer therapeutic strategy for the impact prevention of high fructose injury in age-related malfunctions of the gastric mucosa (GM) in the animal model is important.
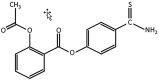
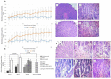
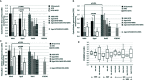
Methods: Adult and aged male rats were divided into control groups (standard diet, SD) and high fructose diet (HFD) groups; acute water immersion restraint stress (WIRS) was induced for evaluation of GM adaptive response and effects of testing the therapeutic potential of H2S-releasing compounds (H2S donors). Histological examination of gastric damage was done on hematoxylin-eosin stained slides. Cystathionine beta-synthase (CBS), Cystathionine gamma-lyase (CSE), and Thiosulfate-dithiol sulfurtransferase (TST) activities and oxidative index were assessed during exogenous administration of H2S donors: sodium hydrosulfide (NaHS) and the novel hybrid H2S-releasing aspirin (ATB-340). The results showed that HFD increased gastric damage in adult and aged rats. HFD-associated malfunction characterized by low activities of H2S key enzymes, inducing increased oxidation. Pretreatment with NaHS, ATB-340 of aged rats in the models of HFD, and WIRS attenuated gastric damage in contrast to vehicle-treated group (p < 0.05). The effect of ATB-340 was characterized by reverse oxidative index and increased CBS, CSE, and TST activities. In conclusion, H2S donors prevent GM age-related malfunctions by enhancement of CBS, CSE, and TST expression against fructose excess injury though reduction of oxidative damage.
Keywords: aging; donor; fructose; gastric mucosa; hydrogen sulfide; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2020 Pavlovskiy, Yashchenko and Zayachkivska.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Mesenteric Adipose Tissue Damage, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Redox Imbalance From High Fructose Diet-Induced Injury in Aged Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 30;12:693100. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.693100. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34526894 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of hydrogen sulfide-releasing naproxen (ATB-346) versus naproxen on formation of stress-induced gastric lesions, the regulation of systemic inflammation, hypoxia and alterations in gastric microcirculation.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017 Oct;68(5):749-756. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 29375050
-
Interaction between endogenous carbon monoxide and hydrogen sulfide in the mechanism of gastroprotection against acute aspirin-induced gastric damage.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Dec;114:235-250. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Nov 5. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27825819
-
Targeting hydrogen sulfide as a promising therapeutic strategy for atherosclerosis.Int J Cardiol. 2014 Mar 15;172(2):313-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2014.01.068. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Int J Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 24491853 Review.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Use of Hydrogen Sulfide to Protect Against Intimal Hyperplasia.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 11;9:876639. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.876639. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35479275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulfur Administration in Fe-S Cluster Homeostasis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Oct 29;10(11):1738. doi: 10.3390/antiox10111738. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34829609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide Prevents Mesenteric Adipose Tissue Damage, Endothelial Dysfunction, and Redox Imbalance From High Fructose Diet-Induced Injury in Aged Rats.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 30;12:693100. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.693100. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34526894 Free PMC article.
-
Thiosulphate sulfurtransferase: Biological roles and therapeutic potential.Redox Biol. 2025 May;82:103595. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2025.103595. Epub 2025 Mar 14. Redox Biol. 2025. PMID: 40107018 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogen Sulfide: A Versatile Molecule and Therapeutic Target in Health and Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Sep 10;14(9):1145. doi: 10.3390/biom14091145. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39334911 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ajayi O. V., Oluwole F. S., Dare A. (2018). Anti-ulcerogenic, antioxidant and mucogenic effects of L-cysteine in gastric tissue of Wistar rats. J. Appl. Life Sci. Int. 14, 1–10. 10.9734/JALSI/2018/45289 - DOI
-
- Bezpalko L., Gavrilyuk O., Zayachkivska O. (2015). Inflammatory response in visceral fat tissue and liver is prenatally programmed: experimental research. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 66 (1), 57–64. - PubMed
-
- Cao X., Bian J. S. (2018). The Signaling Interaction Systems of in NO Biology and H2S and Medicine. Gasotransmitters 12, 145. 10.1039/9781788013000-00145 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

