Communication Among Photoreceptors and the Central Clock Affects Sleep Profile
- PMID: 32848895
- PMCID: PMC7431659
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00993
Communication Among Photoreceptors and the Central Clock Affects Sleep Profile
Abstract
Light is one of the most important factors regulating rhythmical behavior of Drosophila melanogaster. It is received by different photoreceptors and entrains the circadian clock, which controls sleep. The retina is known to be essential for light perception, as it is composed of specialized light-sensitive cells which transmit signal to deeper parts of the brain. In this study we examined the role of specific photoreceptor types and peripheral oscillators located in these cells in the regulation of sleep pattern. We showed that sleep is controlled by the visual system in a very complex way. Photoreceptors expressing Rh1, Rh3 are involved in night-time sleep regulation, while cells expressing Rh5 and Rh6 affect sleep both during the day and night. Moreover, Hofbauer-Buchner (HB) eyelets which can directly contact with s-LN v s and l-LN v s play a wake-promoting function during the day. In addition, we showed that L2 interneurons, which receive signal from R1-6, form direct synaptic contacts with l-LN v s, which provides new light input to the clock network.
Keywords: Drosophila; Hofbauer-Buchner eyelets; peripheral clock; photoreceptors; sleep.
Copyright © 2020 Damulewicz, Ispizua, Ceriani and Pyza.
Figures




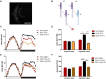

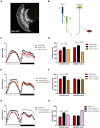


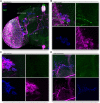
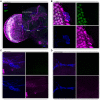
Similar articles
-
Four of the six Drosophila rhodopsin-expressing photoreceptors can mediate circadian entrainment in low light.J Comp Neurol. 2016 Oct 1;524(14):2828-44. doi: 10.1002/cne.23994. Epub 2016 Mar 28. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26972685
-
Autophagy in the retina affects photoreceptor synaptic plasticity and behavior.J Insect Physiol. 2025 Mar;161:104741. doi: 10.1016/j.jinsphys.2024.104741. Epub 2024 Dec 9. J Insect Physiol. 2025. PMID: 39662838
-
A Neural Network Underlying Circadian Entrainment and Photoperiodic Adjustment of Sleep and Activity in Drosophila.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 31;36(35):9084-96. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0992-16.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27581451 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Rhodopsins as Circadian Photoreceptors in the Drosophila melanogaster.Biology (Basel). 2019 Jan 10;8(1):6. doi: 10.3390/biology8010006. Biology (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30634679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Retina and Other Light-sensitive Ocular Clocks.J Biol Rhythms. 2016 Jun;31(3):223-43. doi: 10.1177/0748730416642657. Epub 2016 Apr 19. J Biol Rhythms. 2016. PMID: 27095816 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Better Sleep at Night: How Light Influences Sleep in Drosophila.Front Physiol. 2020 Sep 4;11:997. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00997. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33013437 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Light exposure during development affects physiology of adults in Drosophila melanogaster.Front Physiol. 2022 Nov 25;13:1008154. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.1008154. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36505068 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy as a new player in the regulation of clock neurons physiology of Drosophila melanogaster.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 13;14(1):6085. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56649-3. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38480808 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics of sleep structure in Parkinson's disease patients with hallucinations based on polysomnography.Front Neurol. 2022 Nov 1;13:929569. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.929569. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36388202 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of peripheral clocks: lessons from the fly.FEBS Lett. 2022 Feb;596(3):263-293. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14251. Epub 2021 Dec 16. FEBS Lett. 2022. PMID: 34862983 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

