On-Field Perceptual-Cognitive Training Improves Peripheral Reaction in Soccer: A Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32849142
- PMCID: PMC7427441
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01948
On-Field Perceptual-Cognitive Training Improves Peripheral Reaction in Soccer: A Controlled Trial
Abstract
Abilities such as peripheral reaction are of special importance in soccer. Whether these abilities can be improved by sport-specific on-field interventions remains unclear. The aim of the present controlled trial was to investigate the effect of a soccer-specific perceptual-cognitive on-field training on peripheral reaction of highly talented soccer players aged 12-13 years. N = 38 male elite athletes from young talent centers were allocated to an intervention (n = 19) and a control group (CG) (n = 19). Computer-based peripheral perception tests were conducted before and after intervention. Combining a sport-specific and a juggling task, the intervention was performed once a week (8 weeks, 20 min per week) in addition to team training. The CG exclusively underwent usual team training. Analyses show significant differences between the two groups for peripheral reaction time (PRT), with significant improvements for the intervention group and none for the CG. Furthermore, results indicate that improvements in peripheral reaction might be due to changes in the reaction time of right-footed players. Future studies should be conducted to clarify the effect of sport-specific on-field training approaches on PRT. These analyses should consider the influence of lateralization on effectivity of perceptual-cognitive on-field training approaches.
Keywords: cognition; cognitive component skill approach; expert performance; expert-performance approach; lateralization; perceptual-cognitive training; peripheral reaction; visual perception.
Copyright © 2020 Schumacher, Reer and Braumann.
Figures
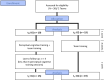

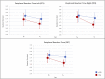
References
-
- Appelbaum G. L., Erickson G. (2016). International review of sport and exercise psychology sports vision training: a review of the state-of-the-art in digital training techniques. Exerc. Psychol. 11 160–189. 10.1080/1750984x.2016.1266376 - DOI
-
- Beek P. J., Jacobs D. M., Daffertshofer A., Huys R. (2003). Expert performance in sport: views from the joint perspectives of ecological psychology and dynamical systems theory. In Expert Performance in Sport eds Starkes J., Ericsson A. (Cahmpaign III: Human Kinetics; ), 321–344
-
- Beek P. J., Lewbel A. (1995). The Science of Juggling. Nat. Commun. 273 92–97. 10.2307/24982089 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

