The First Mitochondrial Genome for Geastrales (Sphaerobolus stellatus) Reveals Intron Dynamics and Large-Scale Gene Rearrangements of Basidiomycota
- PMID: 32849488
- PMCID: PMC7432440
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01970
The First Mitochondrial Genome for Geastrales (Sphaerobolus stellatus) Reveals Intron Dynamics and Large-Scale Gene Rearrangements of Basidiomycota
Abstract
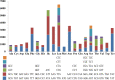
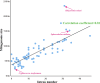
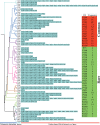
In this study, the mitogenome of artillery fungus, Sphaerobolus stellatus, was assembled and compared with other Basidiomycota mitogenomes. The Sphaerobolus stellatus mitogenome was composed of circular DNA molecules, with a total size of 152,722 bp. Accumulation of intergenic and intronic sequences contributed to the Sphaerobolus stellatus mitogenome becoming the fourth largest mitogenome among Basidiomycota. We detected large-scale gene rearrangements in Basidiomycota mitogenomes, and the Sphaerobolus stellatus mitogenome contains a unique gene order. The quantity and position classes of intron varied between 75 Basidiomycota species we tested, indicating frequent intron loss/gain events occurred in the evolution of Basidiomycota. A novel intron position classes (P1281) was detected in the Sphaerobolus stellatus mitogenome, without any homologous introns from other Basidiomycota species. A pair of fragments with a total length of 9.12 kb in both the nuclear and mitochondrial genomes of Sphaerobolus stellatus was detected, indicating possible gene transferring events. Phylogenetic analysis based on the combined mitochondrial gene set obtained well-supported tree topologies (Bayesian posterior probabilities ≥ 0.99; bootstrap values ≥98). This study served as the first report on the mitogenome from the order Geastrales, which will promote the understanding of the phylogeny, population genetics, and evolution of the artillery fungus, Sphaerobolus stellatus.
Keywords: gene rearrangement; intron; mitochondrial genome; phylogenetic analysis; protein coding gene; repeat sequence.
Copyright © 2020 Ye, Cheng, Ren, Liao and Li.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The 256 kb mitochondrial genome of Clavaria fumosa is the largest among phylum Basidiomycota and is rich in introns and intronic ORFs.IMA Fungus. 2020 Nov 14;11(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s43008-020-00047-7. IMA Fungus. 2020. PMID: 33292749 Free PMC article.
-
Panorama of intron dynamics and gene rearrangements in the phylum Basidiomycota as revealed by the complete mitochondrial genome of Turbinellus floccosus.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021 Mar;105(5):2017-2032. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11153-w. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33555361
-
The 206 kbp mitochondrial genome of Phanerochaete carnosa reveals dynamics of introns, accumulation of repeat sequences and plasmid-derived genes.Int J Biol Macromol. 2020 Nov 1;162:209-219. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.142. Epub 2020 Jun 18. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020. PMID: 32562727
-
The first two mitochondrial genomes for the genus Ramaria reveal mitochondrial genome evolution of Ramaria and phylogeny of Basidiomycota.IMA Fungus. 2022 Sep 13;13(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s43008-022-00100-7. IMA Fungus. 2022. PMID: 36100951 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative mitogenome analysis of two ectomycorrhizal fungi (Paxillus) reveals gene rearrangement, intron dynamics, and phylogeny of basidiomycetes.IMA Fungus. 2020 Jul 2;11:12. doi: 10.1186/s43008-020-00038-8. eCollection 2020. IMA Fungus. 2020. PMID: 32670777 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Organellar Introns in Fungi, Algae, and Plants.Cells. 2021 Aug 6;10(8):2001. doi: 10.3390/cells10082001. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34440770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The 256 kb mitochondrial genome of Clavaria fumosa is the largest among phylum Basidiomycota and is rich in introns and intronic ORFs.IMA Fungus. 2020 Nov 14;11(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s43008-020-00047-7. IMA Fungus. 2020. PMID: 33292749 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative mitochondrial genome analysis reveals intron dynamics and gene rearrangements in two Trametes species.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 28;11(1):2569. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-82040-7. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33510299 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative analyses of Pleurotus pulmonarius mitochondrial genomes reveal two major lineages of mini oyster mushroom cultivars.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024 Feb 1;23:905-917. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2024.01.021. eCollection 2024 Dec. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024. PMID: 38370975 Free PMC article.
-
The first complete chloroplast genome of Fagopyrum leptopodum (Diels) Hedberg (Caryophyllales: Polygonaceae) with phylogenetic implications.Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021 Jul 5;6(8):2203-2205. doi: 10.1080/23802359.2021.1945967. eCollection 2021. Mitochondrial DNA B Resour. 2021. PMID: 34263050 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams K. L., Qiu Y. L., Stoutemyer M., Palmer J. D. (2002). Punctuated evolution of mitochondrial gene content: high and variable rates of mitochondrial gene loss and transfer to the nucleus during angiosperm evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 9905–9912. 10.1073/pnas.042694899 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

