IL-37 Gene Modification Enhances the Protective Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
- PMID: 32849879
- PMCID: PMC7439787
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8883636
IL-37 Gene Modification Enhances the Protective Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Intestinal Ischemia Reperfusion Injury
Abstract
Background: Ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) is the major cause of intestinal damage in clinic. Although either mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) or interleukin 37 (IL-37) shows some beneficial roles to ameliorate IRI, their effects are limited. In this study, the preventative effects of IL-37 gene-modified MSCs (IL-37-MSCs) on intestinal IRI are investigated.
Methods: Intestinal IRI model was established by occluding the superior mesenteric artery for 30 minutes and then reperfused for 72 hours in rats. Forty adult male Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into the sham control, IL-37-MSC-treated, MSC-treated, recombinant IL-37- (rIL-37-) treated, and untreated groups. Intestinal damage was assessed by H&E staining. The levels of gut barrier function factors (diamine oxidase and D-Lactate) and inflammation cytokine IL-1β were assayed using ELISA. The synthesis of tissue damage-related NLRP3 inflammasome and downstream cascade reactions including cleaved caspase-1, IL-1β, and IL-18 was detected by western blot. The mRNA levels of proinflammatory mediators IL-6 and TNF-α, which are downstream of IL-1β and IL-18, were determined by qPCR. Data were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) after the normality test and followed by post hoc analysis with the least significant difference (LSD) test.
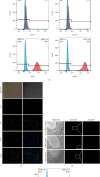
Results: IL-37-MSCs were able to migrate to the damaged tissue and significantly inhibit intestinal IRI. As compared with MSCs or the rIL-37 monotherapy group, IL-37-MSC treatment both improved gut barrier function and decreased local and systemic inflammation cytokine IL-1β level in IRI rats. In addition, tissue damage-related NLRP3 and downstream targets (cleaved caspase-1, IL-1β, and IL-18) were significantly decreased in IRI rats treated with IL-37-MSCs. Furthermore, IL-1β- and IL-18-related proinflammatory mediator IL-6 and TNF-α mRNA expressions were all significantly decreased in IRI rats treated with IL-37-MSCs.
Conclusion: The results suggest that IL-37 gene modification significantly enhances the protective effects of MSCs against intestinal IRI. In addition, NLRP3-related signaling pathways could be associated with IL-37-MSC-mediated protection.
Copyright © 2020 Dejun Kong et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Figures


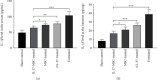


Similar articles
-
Protective effect of IAXO-102 on renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Med Life. 2023 Apr;16(4):623-630. doi: 10.25122/jml-2022-0280. J Med Life. 2023. PMID: 37305825 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogen-Rich Saline Attenuated Subarachnoid Hemorrhage-Induced Early Brain Injury in Rats by Suppressing Inflammatory Response: Possible Involvement of NF-κB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Jul;53(5):3462-3476. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9242-y. Epub 2015 Jun 20. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26091790
-
Mesenchymal stem cells increase antioxidant capacity in intestinal ischemia/reperfusion damage.J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Jul;52(7):1196-1206. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.12.024. Epub 2017 Jan 2. J Pediatr Surg. 2017. PMID: 28118930
-
Role of Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells in Modulating Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: Current State of the Art and Future Perspectives.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 23;11(3):689. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030689. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Probiotics improve intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 May 22;12:1546650. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1546650. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40486191 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IL-37 overexpression promotes endometrial regenerative cell-mediated inhibition of cardiac allograft rejection.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jul 15;13(1):302. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02982-1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35841010 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by MSCs-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles in Rodent Models: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Neural Plast. 2022 Oct 6;2022:3933252. doi: 10.1155/2022/3933252. eCollection 2022. Neural Plast. 2022. PMID: 36338577 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of IL-37 in Human Health and Disease.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 25;12:696605. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.696605. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34248996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The efficacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on rat intestinal immune-function injured by ischemia/reperfusion.Heliyon. 2023 Apr 20;9(5):e15585. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15585. eCollection 2023 May. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37131448 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Autophagy: Potential Targets of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Based Therapies in Ischemic Stroke.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 26;15:641157. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.641157. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33716657 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

