A Study for Expanding Application Sites for Rotigotine Transdermal Patch
- PMID: 32850112
- PMCID: PMC7436353
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5892163
A Study for Expanding Application Sites for Rotigotine Transdermal Patch
Abstract
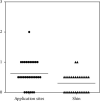
The rotigotine transdermal patch (RTP) is a dopamine agonist used to treat Parkinson's disease (PD). Some PD patients cannot continue RTP treatment due to application site reactions. We explored sites for RTP where application site reactions are less severe than those in the six approved application sites. Thirty PD patients (12 men, mean age = 76 years) who underwent RTP at the approved sites and had some application site reactions were enrolled in this study. When applying the RTP to the approved application sites for more than four weeks (pre-RTP) and then on the shin for the following four weeks (post-RTP), skin reactions, itching evaluated using the skin irritation score, motor symptoms, clinical global impressions scale, and plasma rotigotine concentration were examined. The mean visual analogue scale and skin irritation score in the post-RTP group were significantly lower than those in the pre-RTP group. The mean Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale part III score in the post-RTP group was slightly but significantly lower than that in the pre-RTP group. Plasma rotigotine concentration in the post-RTP group was slightly but significantly lower than that in the pre-RTP group. These results indicate that the shin can be a useful application site for RTP.
Copyright © 2020 Hitoshi Kujirai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this manuscript.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Evaluation of rotigotine transdermal patch for the treatment of apathy and motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease.BMC Neurol. 2016 Jun 7;16:90. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0610-7. BMC Neurol. 2016. PMID: 27267880 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Preventive effect of a heparinoid-containing product on the application site reaction of the rotigotine transdermal patch in Parkinson's disease: A pilot randomized clinical trial (the SkinHeRo study).Clin Park Relat Disord. 2021 Aug 13;5:100105. doi: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2021.100105. eCollection 2021. Clin Park Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 34458718 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of rotigotine transdermal patch for the treatment of depressive symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease.Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016 Aug;17(11):1453-61. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2016.1202917. Epub 2016 Jul 7. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27322571 Clinical Trial.
-
Rotigotine transdermal system for the treatment of Parkinson's disease.Clin Ther. 2008 May;30(5):813-24. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2008.05.007. Clin Ther. 2008. PMID: 18555929 Review.
-
Rotigotine: transdermal dopamine agonist treatment of Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome.Ann Pharmacother. 2007 Feb;41(2):285-95. doi: 10.1345/aph.1H113. Epub 2007 Jan 9. Ann Pharmacother. 2007. PMID: 17213296 Review.
Cited by
-
Translation from Preclinical Research to Clinical Trials: Transdermal Drug Delivery for Neurodegenerative and Mental Disorders.Pharm Res. 2024 Jun;41(6):1045-1092. doi: 10.1007/s11095-024-03718-x. Epub 2024 Jun 11. Pharm Res. 2024. PMID: 38862719 Review.
References
-
- Elshoff J.-P., Braun M., Andreas J.-O., Middle M., Cawello W. Steady-state plasma concentration profile of transdermal rotigotine: an integrated Analysis of three, open-label, randomized, phase I multiple dose studies. Clinical Therapeutics. 2012;34(4):966–978. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2012.02.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Woitalla D., Kassubek J., Timmermann L., et al. Reduction of gastrointestinal symptoms in Parkinson’s disease after a switch from oral therapy to rotigotine transdermal patch: a non-interventional prospective multicenter trial. Parkinsonism & Related Disorders. 2015;21(3):199–204. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.11.024. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

