Overwhelming COVID-19 Sepsis in a Patient With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- PMID: 32850198
- PMCID: PMC7444744
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.9320
Overwhelming COVID-19 Sepsis in a Patient With Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Abstract
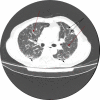
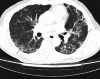
The new disease caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was dubbed coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by the World Health Organization and declared a pandemic. Initially thought to be a pathogen that primarily attacks the lungs, SARS-CoV-2 has turned out to be a much more formidable foe impacting almost every organ and system aggressively. I report the case of a 60-year-old man who came to the ED due to symptoms of high fever, headache, mild confusion, dry cough and exacerbated dyspnea since the last 24 hours. He had a history of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and was undergoing treatment with antifibrotic medication. Apart from IPF, he had no other comorbid. He acquired SARS-CoV-2 infection by close contact and infection deteriorated into pneumonia and septic shock. Complete blood count showed white blood cells at 3.3×103/μL and platelets at 71×103/μL; lymphocyte count was low. Arterial blood gases revealed metabolic acidosis. Definitive diagnosis was by a positive real-time reverse-transcriptase-polymerase-chain-reaction (RT-PCR) assay of nasal and pharyngeal swab specimens, and high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) finding of new-onset ground-glass opacities on the very first day of admission that was the presenting day. The patient became unresponsive and died overnight. As numbers of COVID-19 show an uprise, this case highlights that IPF patients with relatively advanced age need to exercise extra caution because they are at high risk for developing overwhelming COVID-19-linked sepsis, which may be fatal.
Keywords: covid-19; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; severe sepsis.
Copyright © 2020, Akram et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evolving concepts. Ryu JH, Moua T, Daniels CE, Hartman TE, Yi ES, Utz JP, Limper AH. Mayo Clin Proc. 2014;89:1130–1142. - PubMed
-
- Pneumonia of unknown cause - China. [Jan;2020 ];https://www.who.int/csr/don/05-january-2020-pneumonia-of-unkown-cause-ch... 2020
-
- Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it. [Feb;2020 ];https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica... 2020
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
