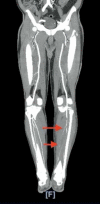
Covid-19 Presenting as Acute Limb Ischemia
- PMID: 32850218
- PMCID: PMC7444888
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.9344
Covid-19 Presenting as Acute Limb Ischemia
Abstract
Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and represents a potentially fatal disease. COVID-19 is associated with a hypercoagulable state leading to increased incidence of venous thromboembolism. Arterial thrombosis has been reported, but the prevalence is not known. Herein, we report an unusual presentation of a 77-year-old male who presented with dyspnea and pain in left leg and was found to have acute limb ischemia. Our case adds to the limited literature regarding arterial thrombosis in COVID-19.
Keywords: acute limb ischemia; arterial thrombosis; covid-19; sars-cov-2 (severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; thrombosis.
Copyright © 2020, Singh et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- A rapid advice guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infected pneumonia (standard version) Jin Y-H, Cai L, Cheng Z-S, et al.; Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University Novel Coronavirus Management and Research Team, Evidence-Based Medicine Chapter of China International Exchange and Promotive Association for Medical and Health Care (CPAM) Mil Med Res. 2020;7:4. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous