Laminins Regulate Placentation and Pre-eclampsia: Focus on Trophoblasts and Endothelial Cells
- PMID: 32850857
- PMCID: PMC7426496
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00754
Laminins Regulate Placentation and Pre-eclampsia: Focus on Trophoblasts and Endothelial Cells
Abstract
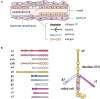
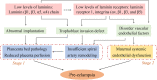
Pre-eclampsia is a systemic vascular disease characterized by new-onset hypertension and/or proteinuria at ≥20 weeks of gestation and leads to high rates of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Despite the incomplete understanding of pre-eclampsia pathophysiology, it is accepted that insufficient spiral artery remodeling and endothelial dysfunction are major contributors. Laminins (LNs) are a vital family of extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules present in basement membranes that provide unique spatial and molecular information to regulate implantation and placentation. LNs interact with cell surface receptors to trigger intracellular signals that affect cellular behavior. This mini-review summarizes the role of LNs in placental development during normal pregnancy. Moreover, it describes how LN deficiency can lead to the pre-eclampsia, which is associated with trophoblast and vascular endothelial dysfunction. New research directions and the prospect of clinical diagnosis of LN deficiency are discussed, and the gaps in basic and clinical research in this field are highlighted.
Keywords: endothelial dysfunction; laminin; placenta; pre-eclampsia; trophoblast.
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Yin, Yu and Zhou.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Defective trophoblast invasion underlies fetal growth restriction and preeclampsia-like symptoms in the stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rat.Mol Hum Reprod. 2017 Jul 1;23(7):509-519. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gax024. Mol Hum Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28402512
-
Oxygen and placental development during the first trimester: implications for the pathophysiology of pre-eclampsia.Placenta. 2000 Mar-Apr;21 Suppl A:S25-30. doi: 10.1053/plac.1999.0522. Placenta. 2000. PMID: 10831118
-
Placental extracellular vesicles and pre-eclampsia.Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021 Feb;85(2):e13297. doi: 10.1111/aji.13297. Epub 2020 Jul 18. Am J Reprod Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32619308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of trophoblast invasion: from normal implantation to pre-eclampsia.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002 Feb 22;187(1-2):233-8. doi: 10.1016/s0303-7207(01)00687-6. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2002. PMID: 11988332 Review.
-
Defective implantation and placentation: laying the blueprint for pregnancy complications.Reprod Biomed Online. 2006 Oct;13(4):591-9. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60649-9. Reprod Biomed Online. 2006. PMID: 17007686 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-TPO-mediated specific features of the placenta immunohistochemical profile and possible mechanisms for fetal loss.Clin Exp Immunol. 2023 Jul 21;213(2):235-242. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxad057. Clin Exp Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37243348 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin-D deficiency as a potential indicator of defective placentation in preeclampsia.Pak J Med Sci. 2024 Dec;40(11):2619-2625. doi: 10.12669/pjms.40.11.9825. Pak J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39634915 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Matrix Influences Gene Expression and Differentiation of Mouse Trophoblast Stem Cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2023 Oct;32(19-20):622-637. doi: 10.1089/scd.2022.0290. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Stem Cells Dev. 2023. PMID: 37463089 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on Extracellular Matrix Involved in the Development of Preeclampsia.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024;25(7):527-538. doi: 10.2174/0113892037284176240302052521. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2024. PMID: 38561606 Review.
-
Downregulation of cathepsin C alleviates endothelial cell dysfunction by suppressing p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway in preeclampsia.Bioengineered. 2022 Feb;13(2):3019-3028. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.2023994. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35037834 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

