Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals
- PMID: 32850871
- PMCID: PMC7431753
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00782
Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Roles of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Stem Cell Fate Decisions and Early Embryonic Development in Mammals.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jan 21;9:640806. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.640806. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 33553192 Free PMC article.
Abstract
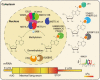
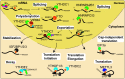
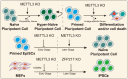
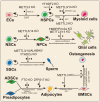
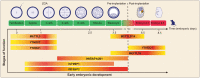
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most abundant internal mRNA modifications, and it affects multiple biological processes related to eukaryotic mRNA. The majority of m6A sites are located in stop codons and 3'UTR regions of mRNAs. m6A regulates RNA metabolism, including alternative splicing (AS), alternative polyadenylation (APA), mRNA export, decay, stabilization, and translation. The m6A metabolic pathway is regulated by a series of m6A writers, erasers and readers. Recent studies indicate that m6A is essential for the regulation of gene expression, tumor formation, stem cell fate, gametogenesis, and animal development. In this systematic review, we summarized the recent advances in newly identified m6A effectors and the effects of m6A on RNA metabolism. Subsequently, we reviewed the functional roles of RNA m6A modification in diverse cellular bioprocesses, such as stem cell fate decisions, cell reprogramming and early embryonic development, and we discussed the potential of m6A modification to be applied to regenerative medicine, disease treatment, organ transplantation, and animal reproduction.
Keywords: N6-methyladenosine; RNA metabolism; cell reprogramming; embryonic development; stem cell fate.
Copyright © 2020 Zhang, Zhai, Zhang, Dai and Li.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

