3D bioprinting spatiotemporally defined patterns of growth factors to tightly control tissue regeneration
- PMID: 32851179
- PMCID: PMC7428335
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abb5093
3D bioprinting spatiotemporally defined patterns of growth factors to tightly control tissue regeneration
Abstract
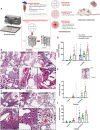
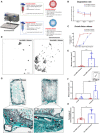
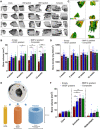
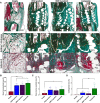
Therapeutic growth factor delivery typically requires supraphysiological dosages, which can cause undesirable off-target effects. The aim of this study was to 3D bioprint implants containing spatiotemporally defined patterns of growth factors optimized for coupled angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Using nanoparticle functionalized bioinks, it was possible to print implants with distinct growth factor patterns and release profiles spanning from days to weeks. The extent of angiogenesis in vivo depended on the spatial presentation of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Higher levels of vessel invasion were observed in implants containing a spatial gradient of VEGF compared to those homogenously loaded with the same total amount of protein. Printed implants containing a gradient of VEGF, coupled with spatially defined BMP-2 localization and release kinetics, accelerated large bone defect healing with little heterotopic bone formation. This demonstrates the potential of growth factor printing, a putative point of care therapy, for tightly controlled tissue regeneration.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures


References
-
- Simons M., Ware J. A., Therapeutic angiogenesis in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 863–871 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Henry T. D., Annex B. H., McKendall G., Azrin M. A., Lopez J. J., Giordano F. J., Shah P. K., Willerson J. T., Benza R. L., Berman D. S., Gibson C. M., Bajamonde A., Rundle A. C., Fine J., McCluskey E.; VIVA Investigators , The VIVA trial: Vascular endothelial growth factor in ischemia for vascular angiogenesis. Circulation 107, 1359–1365 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Shields L. B. E., Raque G. H., Glassman S. D., Campbell M., Vitaz T., Harpring J., Shields C. B., Adverse effects associated with high-dose recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 use in anterior cervical spine fusion. Spine 31, 542–547 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

