Clonal and drug resistance dynamics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pediatric populations in China
- PMID: 32851295
- PMCID: PMC7331318
- DOI: 10.1002/ped4.12129
Clonal and drug resistance dynamics of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in pediatric populations in China
Abstract
Importance: Regional clonal replacements of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) are common. It is necessary to understand the clonal and drug resistance changes in specific areas.
Objective: To evaluate the clonal and drug resistance dynamics of MRSA in Chinese children from 2010 to 2017.
Methods: MRSA was isolated from patients in Beijing Children's Hospital from 2010 to 2013 and from 2016 to 2017. The molecular characteristics and antibiotic resistance were determined.
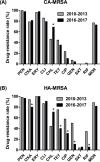
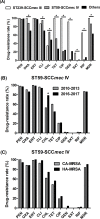
Results: In total, 211 MRSA isolates were collected, and 104 isolates were classified as community-associated MRSA (CA-MRSA). ST59-SCC mec IV was the most prevalent type in both CA-MRSA (65.4%) and healthcare- associated-MRSA (HA-MRSA) (46.7%). ST239-SCC mec III accounted for 21.5% of all HA-MRSA, which were not detected in 2016, and only three isolates were detected in 2017. The pvl gene carrying rate of CA- MRSA was significantly higher than that of HA-MRSA (42.3% vs. 29.0%, P = 0.0456). Among CA-MRSA, resistance rate to all tested antibiotics excluding chloramphenicol remained stable over the periods of 2010-2013 and 2016-2017. HA-MRSA displayed an overall trend of decreased resistance to oxacillin, gentamicin, tetracycline, ciprofloxacin, and rifampin, and increased resistance to chloramphenicol, consistent with the difference of antibiotic resistance patterns between ST59-SCC mec IV and ST239-SCC mec III isolates. Vancomycin minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) creep was found in the study period in all MRSA and ST59-SCC mec IV isolates.
Interpretation: ST59-SCC mec IV has spread to hospitals and replaced the traditional ST239-SCC mec III clone, accompanied by changes in drug resistance. Furthermore, vancomycin MIC creep indicated that the rational use of antibiotics should be seriously considered.
Keywords: China; Clonal lineage; Drug resistance; Methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA); Pediatric.
© 2019 Chinese Medical Association. Pediatric Investigation published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Futang Research Center of Pediatric Development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
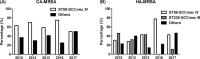

Similar articles
-
[Changes over time in the distribution of dominant clonal complexes of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Medellín, Colombia].Biomedica. 2014 Apr;34 Suppl 1:34-40. doi: 10.1590/S0120-41572014000500005. Biomedica. 2014. PMID: 24968034 Spanish.
-
[Molecular characteristics of methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from Chinese children].Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012 Jan;50(1):38-44. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 22456074 Chinese.
-
Molecular typing revealed the emergence of pvl-positive sequence type 22 methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus in Urumqi, Northwestern China.Infect Drug Resist. 2019 Jun 20;12:1719-1728. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S202906. eCollection 2019. Infect Drug Resist. 2019. PMID: 31354320 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular epidemiology and characteristic of virulence gene of community-acquired and hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates in Sun Yat-sen Memorial hospital, Guangzhou, Southern China.BMC Infect Dis. 2016 Jul 22;16:339. doi: 10.1186/s12879-016-1684-y. BMC Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27450316 Free PMC article.
-
Methicillin/Oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus as a hospital and public health threat in Brazil.Braz J Infect Dis. 2010 Jan-Feb;14(1):71-6. doi: 10.1590/s1413-86702010000100014. Braz J Infect Dis. 2010. PMID: 20428658 Review.
Cited by
-
In Vitro Activity of Vancomycin, Teicoplanin, Linezolid and Daptomycin Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Isolates Collected from Chinese Hospitals in 2018-2020.Infect Drug Resist. 2021 Dec 16;14:5449-5456. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S340623. eCollection 2021. Infect Drug Resist. 2021. PMID: 34949928 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum.Pediatr Investig. 2020 Mar 17;4(1):64. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12173. eCollection 2020 Mar. Pediatr Investig. 2020. PMID: 32852486 Free PMC article.
-
Clonal diversity of Staphylococcus aureus isolates in clinical specimens from selected health facilities in Ethiopia.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Jun 12;23(1):399. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08380-z. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37308817 Free PMC article.
-
Transcription tuned by S-nitrosylation underlies a mechanism for Staphylococcus aureus to circumvent vancomycin killing.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 21;14(1):2318. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37949-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37085493 Free PMC article.
-
Desiccation tolerance and reduced antibiotic resistance: Key drivers in ST239-III to ST22-IV MRSA clonal replacement at a Malaysian teaching hospital.Int J Med Microbiol. 2024 Dec;317:151638. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2024.151638. Epub 2024 Oct 13. Int J Med Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39437562 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Porto JP, Santos RO, Gontijo Filho PP, Ribas RM. Active surveillance to determine the impact of methicillin resistance on mortality in patients with bacteremia and influences of the use of antibiotics on the development of MRSA infection. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2013;46:713‐718. - PubMed
-
- Gasch O, Camoez M, Dominguez MA, Padilla B, Pintado V, Almirante B, et al. Predictive factors for mortality in patients with methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infection: impact on outcome of host, microorganism and therapy. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2013;19:1049‐1057. - PubMed
-
- Rojo P, Barrios M, Palacios A, Gomez C, Chaves F. Community‐associated Staphylococcus aureus infections in children. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2010;8:541‐554. - PubMed
-
- Otter JA, French GL. Community‐associated methicillin‐resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains as a cause of healthcare‐associated infection. J Hosp Infect. 2011;79:189‐193. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
