Surfactant protein C dysfunction with new clinical insights for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and autoimmunity
- PMID: 32851322
- PMCID: PMC7331417
- DOI: 10.1002/ped4.12162
Surfactant protein C dysfunction with new clinical insights for diffuse alveolar hemorrhage and autoimmunity
Abstract
Importance: Surfactant protein C (SP-C) dysfunction is a rare disease associated with interstitial lung disease. Early therapies may improve outcomes but the diagnosis is often delayed owing to variability of manifestations.
Objective: To investigate the manifestations and outcomes of SP-C dysfunction.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the records of five pediatric patients who were diagnosed with SP-C dysfunction between February 2014 and April 2017 at Beijing Children's Hospital.
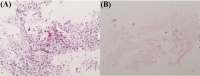
Results: The five patients included two boys and three girls with a median age at diagnosis of 1.3 years. All patients presented with interstitial lung disease and had a heterozygous SFTPC mutation, including an I73T mutation in three patients, a V39L mutation in one patient, and a Y104H mutation in one patient. In addition to common respiratory manifestations, hemoptysis and anemia were observed in one patient with the I73T mutation. Elevated levels of autoantibodies and a large number of hemosiderin-laden macrophages in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid were found in two patients with the I73T mutation, suggesting the presence of diffuse alveolar hemorrage and autoimmunity. Chest high-resolution computed tomography features included ground-glass opacities, reticular opacities, cysts, and pleural thickening. Transbronchial lung biopsy was performed in one patient with the I73T mutation, which revealed the presence of some hemosiderin-laden macrophages in alveolar spaces. All patients received treatment with corticosteroids; two received combined treatment with hydroxychloroquine. During follow-up, the two patients who received hydroxychloroquine showed improved symptoms; of the remaining three patients, two died after their families refused further treatment, while the final patient was lost to follow-up.
Interpretation: This is the first report to describe a new phenotype of diffuse alveolar hemorrhage with autoimmunity in patients with I73T SFTPC mutation. Treatment with hydroxychloroquine should be considered for patients with SP-C dysfunction.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage; Interstitial lung disease; Rheumatoid arthritis; Surfactant protein C.
© 2019 Chinese Medical Association. Pediatric Investigation published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Futang Research Center of Pediatric Development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have indicated no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Nogee LM, Dunbar AE, Wert SE, Askin F, Hamvas A, Whitsett JA. A mutation in the surfactant protein C gene associated with familial interstitial lung disease. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:573‐579. - PubMed
-
- Thomas AQ, Lane K, Phillips J III, Prince M, Markin C, Speer M, et al. Heterozygosity for a surfactant protein C gene mutation associated with usual interstitial pneumonitis and cellular nonspecific interstitial pneumonitis in one kindred. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:1322‐1328. - PubMed
-
- Nogee LM, Dunbar AE III, Wert SE, Askin F, Hamvas A, Whisett JA. Mutations in the surfactant protein C gene associated with interstitial lung disease. Chest. 2002;121:20S‐21S. - PubMed
-
- Brasch F, Griese M, Tredano M, Johnen G, Ochs M, Rieger C, et al. Interstitial lung disease in a baby with a de novo mutation in the SFTPC gene. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:30‐39. - PubMed
-
- Cameron HS, Somaschini M, Carrera P, Hamvas A, Whitsett JA, Wert SE, et al. A common mutation in the surfactant protein C gene associated with lung disease. J Pediatr. 2005;146:370‐375. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
