WISP1 alleviates lipid deposition in macrophages via the PPARγ/CD36 pathway in the plaque formation of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 32851768
- PMCID: PMC7579692
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15783
WISP1 alleviates lipid deposition in macrophages via the PPARγ/CD36 pathway in the plaque formation of atherosclerosis
Abstract
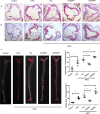
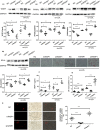
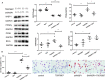
Lipid deposition in macrophages plays an important role in atherosclerosis. The WNT1-inducible signalling pathway protein 1(WISP1) can promote proliferation and migration of smooth muscle cells. Its expression is up-regulated in obesity, which is associated with atherosclerosis, but the effect of WISP1 on atherosclerosis remains unclear. Thus, the objective of our study was to elucidate the role of WISP and its mechanism of action in atherosclerosis via in vivo and in vitro experiments. In our experiment, ApoE-/- mice were divided into 5 groups: control, high-fat diet (HFD), null lentivirus (HFD + NC), lentivirus WISP1 (HFD + IvWISP1) and WISP1-shRNA (HFD + shWISP1). Oil Red O staining, immunofluorescence and immunohistochemistry of the aortic sinuses were conducted. Macrophages (RAW264.7 cell lines and peritoneal macrophages) were stimulated with 50 μg/mL oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL); then, the reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was measured. Oil Red O staining and Dil-ox-LDL (ox-LDL with Dil dye) uptake measurements were used to test lipid deposition of peritoneal macrophages. WISP1, CD36, SR-A and PPARγ expression levels were measured via Western blotting and ELISA. The results showed that HFD mice had increased WISP1, CD36 and SR-A levels. The plaque lesion area increased when WISP1 was down-regulated, and lipid uptake and foam cell formation were inhibited when WISP1 was up-regulated. Treatment of RAW264.7 cell lines with ox-LDL increased WISP1 expression via activation of the Wnt5a/β-catenin pathway, whereas ROS inhibition reduced WISP1 expression. Moreover, WISP1 down-regulated CD36 and SR-A expression, and Oil Red O staining and Dil-ox-LDL uptake measurement showed that WISP1 down-regulated lipid deposition in macrophages. These results clearly demonstrate that WISP1 is activated by ox-LDL at high ROS levels and can alleviate lipid deposition in atherosclerosis through the PPARγ/CD36 pathway.
Keywords: CD36; PPRAγ; SR-A; WISP1; atherosclerosis; lipid deposition; macrophage.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Ertugliflozin attenuates atherosclerosis in nondiabetic ApoE-/- mice by upregulating ABCA1 and LDLR via the PPARγ/LXRα pathway.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025 Oct;1871(7):167927. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2025.167927. Epub 2025 May 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2025. PMID: 40419168
-
WNT1-inducible signalling pathway protein 1 stabilizes atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice via the focal adhesion kinase/mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway.J Hypertens. 2022 Sep 1;40(9):1666-1681. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000003195. Epub 2022 Jul 25. J Hypertens. 2022. PMID: 35881419
-
Inhibition of macrophage-derived foam cells by Adipsin attenuates progression of atherosclerosis.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Dec 1;1868(12):166533. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2022.166533. Epub 2022 Sep 5. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 36064133
-
CD36 in Atherosclerosis: Pathophysiological Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020 Aug 9;22(10):59. doi: 10.1007/s11883-020-00870-8. Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2020. PMID: 32772254 Review.
-
Emerging roles of calpain proteolytic systems in macrophage cholesterol handling.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017 Aug;74(16):3011-3021. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2528-7. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2017. PMID: 28432377 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Compounds from Traditional Chinese Medicine in Modulating Macrophage Cholesterol Metabolism for Atherosclerosis Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jul 25;18(8):1113. doi: 10.3390/ph18081113. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40872505 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Knockdown of ADAMDEC1 ameliorates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury and atherosclerosis progression.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Dec 8;24(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01278-8. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 38063920
-
Oral Nanoformulations in Cardiovascular Medicine: Advances in Atherosclerosis Treatment.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 10;17(7):919. doi: 10.3390/ph17070919. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39065770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalein inhibits macrophage lipid accumulation and inflammatory response by activating the PPARγ/LXRα pathway.Clin Exp Immunol. 2022 Sep 29;209(3):316-325. doi: 10.1093/cei/uxac062. Clin Exp Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35749304 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Wnt1-Inducible signalling pathway Protein-1 levels are associated with cerebral infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.J Endocrinol Invest. 2025 Jul 28. doi: 10.1007/s40618-025-02662-w. Online ahead of print. J Endocrinol Invest. 2025. PMID: 40719953
References
-
- Ross R. Atherosclerosis–an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115‐126. - PubMed
-
- Chistiakov DA, Melnichenko AA, Myasoedova VA, Grechko AV, Orekhov AN. Mechanisms of foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. J Mol Med. 2017;95:1153‐1165. - PubMed
-
- Ogura M, Hori M, Harada‐Shiba M. Association between cholesterol efflux capacity and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36:181‐188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

