Paramagnetic Shifts and Guest Exchange Kinetics in ConFe4- n Metal-Organic Capsules
- PMID: 32851844
- PMCID: PMC7649716
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.0c01816
Paramagnetic Shifts and Guest Exchange Kinetics in ConFe4- n Metal-Organic Capsules
Abstract
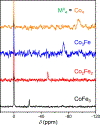
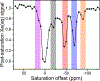
We investigate the magnetic resonance properties and exchange kinetics of guest molecules in a series of hetero-bimetallic capsules, [ConFe4-nL6]4- (n = 1-3), where L2- = 4,4'-bis[(2-pyridinylmethylene)amino]-[1,1'-biphenyl]-2,2'-disulfonate. H bond networks between capsule sulfonates and guanidinium cations promote the crystallization of [ConFe4-nL6]4-. The following four isostructural crystals are reported: two guest-free forms, (C(NH2)3)4[Co1.8Fe2.2L6]·69H2O (1) and (C(NH2)3)4[Co2.7Fe1.3L6]·73H2O (2), and two Xe- and CFCl3-encapsulated forms, (C(NH2)3)4[(Xe)0.8Co1.8Fe2.2L6]·69H2O (3) and (C(NH2)3)4[(CFCl3)Co2.0Fe2.0L6]·73H2O (4), respectively. Structural analyses reveal that Xe induces negligible structural changes in 3, while the angles between neighboring phenyl groups expand by ca. 3° to accommodate the much larger guest, CFCl3, in 4. These guest-encapsulated [ConFe4-nL6]4- molecules reveal 129Xe and 19F chemical shift changes of ca. -22 and -10 ppm at 298 K, respectively, per substitution of low-spin FeII by high-spin CoII. Likewise, the temperature dependence of the 129Xe and 19F NMR resonances increases by 0.1 and 0.06 ppm/K, respectively, with each additional paramagnetic CoII center. The optimal temperature for hyperpolarized (hp) 129Xe chemical exchange saturation transfer (hyper-CEST) with [ConFe4-nL6]4- capsules was found to be inversely proportional to the number of CoII centers, n, which is consistent with the Xe chemical exchange accelerating as the portals expand. The systematic study was facilitated by the tunability of the [M4L6]4- capsules, further highlighting these metal-organic systems for developing responsive sensors with highly shifted 129Xe resonances.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Paramagnetic Organocobalt Capsule Revealing Xenon Host-Guest Chemistry.Inorg Chem. 2020 Oct 5;59(19):13831-13844. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b03634. Epub 2020 Mar 24. Inorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32207611 Free PMC article.
-
Thermally Tunable Adsorption of Xenon in Crystalline Molecular Sorbent.J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023 Jul 20;127(28):13810-13816. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.3c02054. Epub 2023 Jul 10. J Phys Chem C Nanomater Interfaces. 2023. PMID: 39027347 Free PMC article.
-
Hyper-CEST NMR of metal organic polyhedral cages reveals hidden diastereomers with diverse guest exchange kinetics.Nat Commun. 2022 Mar 31;13(1):1708. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-29249-w. Nat Commun. 2022. PMID: 35361759 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative evaluation of pulmonary gas-exchange function using hyperpolarized 129 Xe CEST MRS and MRI.NMR Biomed. 2018 Sep;31(9):e3961. doi: 10.1002/nbm.3961. Epub 2018 Jul 24. NMR Biomed. 2018. PMID: 30040165
-
Bacterial spore detection and analysis using hyperpolarized 129Xe chemical exchange saturation transfer (Hyper-CEST) NMR.Chem Sci. 2014 Aug 1;5(8):3197-3203. doi: 10.1039/c4sc01190b. Chem Sci. 2014. PMID: 25089181 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Coloring ultrasensitive MRI with tunable metal-organic frameworks.Chem Sci. 2021 Feb 9;12(12):4300-4308. doi: 10.1039/d0sc06969h. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34163694 Free PMC article.
-
Multivariate metal-organic frameworks enable chemical shift-encoded MRI with femtomolar sensitivity for biological systems.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 24;16(1):6832. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-62110-4. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40707454 Free PMC article.
-
31P ParaCEST: 31P MRI-CEST Imaging Based on the Formation of a Ternary Adduct between Inorganic Phosphate and Eu-DO3A.Inorg Chem. 2022 Dec 12;61(49):19663-19667. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.2c03329. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Inorg Chem. 2022. PMID: 36445702 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperpolarized Xenon-129 Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (HyperCEST) Molecular Imaging: Achievements and Future Challenges.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1939. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031939. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339217 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryptophane-xenon complexes for 129Xe MRI applications.RSC Adv. 2021;11(13):7693-7703. doi: 10.1039/d0ra10765d. Epub 2021 Feb 17. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 34745572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wolber J; Rowland IJ; Leach MO; Bifone A Intravascular Delivery of Hyperpolarized 129Xenon for In Vivo MRI. Appl. Magn. Reson. 1998, 15, 343–352.
- Gil A; Korili SA; Vicente MA Recent Advances in the Control and Characterization of the Porous Structure of Pillared Clay Catalysts. Catal. Rev. 2008, 50, 153–221.
- Couch MJ; Blasiak B; Tomanek B; Ouriadov AV; Fox MS; Dowhos KM; Albert MS Hyperpolarized and Inert Gas MRI: The Future. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2015, 17, 149–162. - PubMed
- Banerjee D; Simon CM; Elsaidi SK; Haranczyk M; Thallapally PK Xenon Gas Separation and Storage Using Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem 2018, 4, 466–494.
-
- Bhaskar ND; Happer W; McClelland T Efficiency of Spin Exchange Between Rubidium Spins and 129Xe Nuclei in a Gas. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 25–28.
- Happer W; Miron E; Schaefer S; Schreiber D; van Wijngaarden WA; Zeng X Polarization of the Nuclear Spins of Noble-Gas Atoms by Spin Exchange with Optically Pumped Alkali-Metal Atoms. Phys. Rev. A 1984, 29, 3092–3110.
- Raftery D; Long H; Meersmann T; Grandinetti PJ; Reven L; Pines A High-Field NMR of Adsorbed Xenon Polarized by Laser Pumping. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1991, 66, 584–587. - PubMed
- Cates GD; Fitzgerald RJ; Barton AS; Bogorad P; Gatzke M; Newbury NR; Saam B Rb-129Xe Spin-Exchange Rates Due to Binary and Three-Body Collisions at High Xe Pressures. Phys. Rev. A 1992, 45, 4631–4639. - PubMed
- Walker TG; Happer W Spin-Exchange Optical Pumping of Noble-Gas Nuclei. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1997, 69, 629–642.
-
- Schröder L Xenon for NMR Biosensing – Inert But Alert. Phys. Med. 2013, 29, 3–16. - PubMed
-
-
Selected examples:
- Kitani S; Takada J Adsorption of Krypton and Xenon on Various Adsorbents. J. Nucl. Sci. Technol. 1965, 2, 51–56.
- Kuznicki SM; Ansón A; Koenig A; Kuznicki TM; Haastrup T; Eyring EM; Hunter D Xenon Adsorption on Modified ETS-10. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 1560–1562.
- Meek ST; Teich-McGoldrick SL; Perry JJ; Greathouse JA; Allendorf MD Effects of Polarizability on the Adsorption of Noble Gases at Low Pressures in Monohalogenated Isoreticular Metal–Organic Frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 19765–19772
- Parkes MV; Staiger CL; Perry JJ; Allendorf MD; Greathouse JA Screening Metal–Organic Frameworks for Selective Noble Gas Adsorption in Air: Effect of Pore Size and Framework Topology. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9093–9106. - PubMed
- Liu J; Fernandes CA; Martin PF; Thallapally PK; Strachan DM A Two-Column Method for the Separation of Kr and Xe from Process Off-Gases. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2014, 53, 12893–12899.
- Feng X; Zong Z; Elsaidi SK; Jasinski JB; Krishna R; Thallapally PK; Carreon MA Kr/Xe Separation Over a Chabazite Zeolite Membrane. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9791–9794. - PubMed
- Kapelewski MT; Oktawiec J; Runčevski T; Gonzalez MI; Long JR Separation of Xenon and Krypton in the Metal–Organic Frameworks M2(m-dobdc) (M=Co, Ni). Isr. J. Chem. 2018, 58, 1138–1143.
- Li L; Guo L; Zhang Z; Yang Q; Yang Y; Bao Z; Ren Q; Li J A Robust Squarate-Based Metal–Organic Framework Demonstrates Record-High Affinity and Selectivity for Xenon Over Krypton. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 9358–9364. - PubMed
-
-
-
Selected examples:
- Chambers JM; Hill PA; Aaron JA; Han Z; Christianson DW; Kuzma NN; Dmochowski IJ Cryptophane Xe-129 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Biosensors Targeting Human Carbonic Anhydrase. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 563–569. - PMC - PubMed
- Kotera N; Tassali N; Léonce E; Boutin C; Berthault P; Brotin T; Dutasta J-P; Delacour L; Traoré T; Buisson D-A; Taran F; Coudert S; Rousseau B A Sensitive Zinc-Activated 129Xe MRI Probe. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 4100–4103. - PubMed
- Palaniappan KK; Francis MB; Pines A; Wemmer DE Molecular Sensing Using Hyperpolarized Xenon NMR Spectroscopy. Isr. J. Chem. 2014, 54, 104–112.
- Joseph AI; El-Ayle G; Boutin C; Léonce E; Berthault P; Holman KT Rim-Functionalized Cryptophane-111 Derivatives via Heterocapping, and Their Xenon Complexes. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15905–15908. - PubMed
- Klippel S; Döpfert J; Jayapaul J; Kunth M; Rossella F; Schnurr M; Witte C; Freund C; Schröder L Cell Tracking with Caged Xenon: Using Cryptophanes as MRI Reporters upon Cellular Internalization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 493–496. - PubMed
- Wang Y; Dmochowski IJ An Expanded Palette of Xenon-129 NMR Biosensors. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2179–2187. - PMC - PubMed
-
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

