Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and complications of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
- PMID: 32851877
- PMCID: PMC7493723
- DOI: 10.2217/fmb-2020-0110
Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and complications of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
Abstract
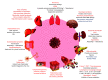
Aim: Despite the similarities in the pathogenesis of the beta coronaviruses, the precise infective mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 remain unclear. Objective: In this review, we aim to focus on the proposed theories behind the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 and highlight the clinical complications related to COVID-19. Methods: We conducted a literature search in Pubmed, Scopus and Google Scholar for the relevant articles regarding clinical complications and pathogenesis of COVID-19. Results: Related articles were included and discussed. Conclusion: Respiratory system and the lungs are the most commonly involved sites of COVID-19 infection. Cardiovascular, liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems are involved with different frequencies and degrees of severity.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; clinical complications; coronavirus disease 2019; pathogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) situation report. (2020). http://www.who.int/Docs/Default-Source/Coronaviruse/Situation-Reports/20...
-
- Centers for disease control and prevention. Symptoms of coronavirus. (2020). http://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
