Neurofilament light as an outcome predictor after cardiac arrest: a post hoc analysis of the COMACARE trial
- PMID: 32852582
- PMCID: PMC7782453
- DOI: 10.1007/s00134-020-06218-9
Neurofilament light as an outcome predictor after cardiac arrest: a post hoc analysis of the COMACARE trial
Abstract
Purpose: Neurofilament light (NfL) is a biomarker reflecting neurodegeneration and acute neuronal injury, and an increase is found following hypoxic brain damage. We assessed the ability of plasma NfL to predict outcome in comatose patients after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA). We also compared plasma NfL concentrations between patients treated with two different targets of arterial carbon dioxide tension (PaCO2), arterial oxygen tension (PaO2), and mean arterial pressure (MAP).
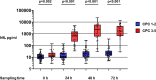
Methods: We measured NfL concentrations in plasma obtained at intensive care unit admission and at 24, 48, and 72 h after OHCA. We assessed neurological outcome at 6 months and defined a good outcome as Cerebral Performance Category (CPC) 1-2 and poor outcome as CPC 3-5.
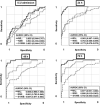
Results: Six-month outcome was good in 73/112 (65%) patients. Forty-eight hours after OHCA, the median NfL concentration was 19 (interquartile range [IQR] 11-31) pg/ml in patients with good outcome and 2343 (587-5829) pg/ml in those with poor outcome, p < 0.001. NfL predicted poor outcome with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.98 (95% confidence interval [CI] 0.97-1.00) at 24 h, 0.98 (0.97-1.00) at 48 h, and 0.98 (0.95-1.00) at 72 h. NfL concentrations were lower in the higher MAP (80-100 mmHg) group than in the lower MAP (65-75 mmHg) group at 48 h (median, 23 vs. 43 pg/ml, p = 0.04). PaCO2 and PaO2 targets did not associate with NfL levels.
Conclusions: NfL demonstrated excellent prognostic accuracy after OHCA. Higher MAP was associated with lower NfL concentrations.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Cardiac arrest; Neurofilament light (NfL); Prognostication.
Conflict of interest statement
Markus Skrifvars reports speakers’ fees and travel grants from BARD Medical (Ireland) and a research grant from GE Healthcare. Kaj Blennow has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, Biogen, Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Roche Diagnostics, and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. Henrik Zetterberg has served at scientific advisory boards for Denali, Roche Diagnostics, Wave, Samumed and CogRx, has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Fujirebio, Alzecure and Biogen, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program.
Figures
Comment in
-
Neurofilament to predict post-anoxic neurological outcome: are we ready for the prime time?Intensive Care Med. 2021 Jan;47(1):77-79. doi: 10.1007/s00134-020-06309-7. Epub 2020 Nov 9. Intensive Care Med. 2021. PMID: 33169216 No abstract available.
References
-
- Nolan JP, Berg RA, Callaway CW, Morrison LJ, Nadkarni V, Perkins GD, Sandroni C, Skrifvars MB, Soar J, Sunde K, Cariou A. The present and future of cardiac arrest care: international experts reach out to caregivers and healthcare authorities. Intensive Care Med. 2018;44:823–832. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5230-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nolan JP, Soar J, Cariou A, Cronberg T, Moulaert VR, Deakin CD, Bottiger BW, Friberg H, Sunde K, Sandroni C, European Resuscitation C, European Society of Intensive Care M European Resuscitation Council and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine 2015 guidelines for post-resuscitation care. Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:2039–2056. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-4051-3. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- TYH2018227/Helsingin ja Uudenmaan Sairaanhoitopiiri
- 2018, 2019/Stiftelsen Dorothea Olivia, Karl Walter och Jarl Walter Perkléns Minne
- 2018, 2019/Medicinska Understödsföreningen Liv och Hälsa
- #2017-00915/Swedish Reserach Council
- #AF-742881/The Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- #FO2017-0243/Hjärnfonden
- #2018-02532/Swedish Research Council
- #ALFGBG-720931/Swedish State Support for Clinical Research
- (#201809-2016862/Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation
- #ALFGBG-715986/the Swedish state under the agreement between the Swedish government and the County Councils, the ALF-agreement
- JPND2019-466-236/European Union Joint Program for Neurodegenerative Disorders
- #681712/ERC_/European Research Council/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

