Factors associated with spoken language comprehension in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review
- PMID: 32852786
- PMCID: PMC7692918
- DOI: 10.1111/dmcn.14651
Factors associated with spoken language comprehension in children with cerebral palsy: a systematic review
Abstract
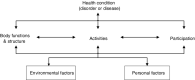
Aim: To identify factors that are relevant for spoken language comprehension in children with cerebral palsy (CP), following the International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health - Children and Youth (ICF-CY) framework.
Method: A systematic literature search was conducted using the electronic literature databases PubMed, Embase, PsycInfo, and Cochrane Library, from January 1967 to December 2019. Included studies involved children with CP, results regarding spoken language comprehension, and analysis of at least one associated factor. Factors were classified within ICF-CY domains.
Results: Twenty-one studies met inclusion criteria. Factors in the ICF-CY domains of body functions and structure were most frequently reported. White brain matter abnormalities, motor type, functional mobility, and intellectual functioning appear to be relevant factors in spoken language comprehension in CP. Factors in the domain of activities and participation, as well as contextual factors, have rarely been studied in the context of spoken language comprehension in CP.
Interpretation: Most factors known to be important for spoken language comprehension in typically developing children and/or known to be susceptible to change by interventions are understudied in CP.
© 2020 The Authors. Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Mac Keith Press.
Figures
References
-
- Coleman A, Weir KA, Ware RS, Boyd RN. Relationship between communication skills and gross motor function in preschool‐aged children with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 2013; 94: 2210–7. - PubMed
-
- Compagnone E, Maniglio J, Camposeo S, et al. Functional classifications for cerebral palsy: correlations between the gross motor function classification system (GMFCS), the manual ability classification system (MACS) and the communication function classification system (CFCS). Res Dev Disabil 2014; 35: 2651–7. - PubMed
-
- Voorman JM, Dallmeijer AJ, Van Eck M, Schuengel C, Becher JG. Social functioning and communication in children with cerebral palsy: association with disease characteristics and personal and environmental factors. Dev Med Child Neurol 2010; 52: 441–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous