Analysis of very-high surface area 3D-printed media in a moving bed biofilm reactor for wastewater treatment
- PMID: 32853235
- PMCID: PMC7451639
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238386
Analysis of very-high surface area 3D-printed media in a moving bed biofilm reactor for wastewater treatment
Abstract
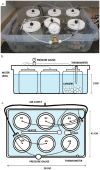
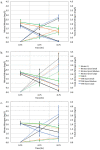
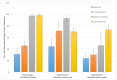
Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBRs) can efficiently treat wastewater by incorporating suspended biocarriers that provide attachment surfaces for active microorganisms. The performance of MBBRs for wastewater treatment is, among other factors, contingent upon the characteristics of the surface area of the biocarriers. Thus, novel biocarrier topology designs can potentially increase MBBR performance in a significant manner. The goal of this work is to assess the performance of 3-D-printed biofilter media biocarriers with varying surface area designs for use in nitrifying MBBRs for wastewater treatment. Mathematical models, rendering, and 3D printing were used to design and fabricate gyroid-shaped biocarriers with a high degree of complexity at three different levels of specific surface area (SSA), generally providing greater specific surface areas than currently available commercial designs. The biocarriers were inoculated with a nitrifying bacteria community, and tested in a series of batch reactors for ammonia conversion to nitrate, in three different experimental configurations: constant fill ratio, constant total surface area, and constant biocarrier media count. Results showed that large and medium SSA gyroid biocarriers delivered the best ammonia conversion performance of all designs, and significantly better than that of a standard commercial design. The percentage of ammonia nitrogen conversion at 8 hours for the best performing biocarrier design was: 99.33% (large SSA gyroid, constant fill ratio), 94.74% (medium SSA gyroid, constant total surface area), and 92.73% (large SSA gyroid, constant biocarrier media count). Additionally, it is shown that the ammonia conversion performance was correlated to the specific surface area of the biocarrier, with the greatest rates of ammonia conversion (99.33%) and nitrate production (2.7 mg/L) for manufactured gyroid biocarriers with a specific surface area greater than 1980.5 m2/m3. The results suggest that the performance of commercial MBBRs for wastewater treatment can be greatly improved by manipulation of media design through topology optimization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Brinkley J, Johnson C, Souza R. Moving bed bio film reactor technology-a full-scale installation for treatment of pharmaceutical wastewater. Chemical Business. 2008;77:50–8.
-
- Mahmoudkhani R, Azar AM, Dehghani A, Goreishi H, editors. Treatment of Contaminated Waters with Petroleum by Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor (MBBR). International Conference on Life Science and Engineering, 107763/IPCBEE; 2012.
-
- Qaderi F, Sayahzadeh A, Azizi M. Efficiency optimization of petroleum wastewater treatment by using of serial moving bed biofilm reactors. Journal of Cleaner Production. 2018;192:665–77. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.04.257 - DOI
-
- Rusten B, Mattsson E, Broch-Due A, Westrum T. Treatment of pulp and paper industry wastewaters in novel moving bed biofilm reactors. Water Science and Technology. 1994;30(3):161 10.2166/wst.1994.0091 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

