Development and evaluation of a rapid CRISPR-based diagnostic for COVID-19
- PMID: 32853291
- PMCID: PMC7451577
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1008705
Development and evaluation of a rapid CRISPR-based diagnostic for COVID-19
Abstract
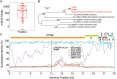
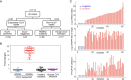
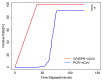
The recent outbreak of human infections caused by SARS-CoV-2, the third zoonotic coronavirus has raised great public health concern globally. Rapid and accurate diagnosis of this novel pathogen posts great challenges not only clinically but also technologically. Metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) and reverse-transcription PCR (RT-PCR) have been the most commonly used molecular methodologies. However, each has their own limitations. In this study, we developed an isothermal, CRISPR-based diagnostic for COVID-19 with near single-copy sensitivity. The diagnostic performances of all three technology platforms were also compared. Our study aimed to provide more insights into the molecular detection of SARS-CoV-2, and also to present a novel diagnostic option for this new emerging virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
iSCAN: An RT-LAMP-coupled CRISPR-Cas12 module for rapid, sensitive detection of SARS-CoV-2.Virus Res. 2020 Oct 15;288:198129. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198129. Epub 2020 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2020. PMID: 32822689 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting SARS-CoV-2 at point of care: preliminary data comparing loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) to polymerase chain reaction (PCR).BMC Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 20;20(1):783. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05484-8. BMC Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 33081710 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and visual detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) by a reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assay.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020 Jun;26(6):773-779. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.04.001. Epub 2020 Apr 8. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32276116 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Perspective Diagnostic Techniques for COVID-19.ACS Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 14;6(8):1998-2016. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.0c00365. Epub 2020 Aug 4. ACS Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32677821 Review.
-
Recent advances in the nucleic acid-based diagnostic tool for coronavirus.Mol Biol Rep. 2020 Nov;47(11):9033-9041. doi: 10.1007/s11033-020-05889-3. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Mol Biol Rep. 2020. PMID: 33025503 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel viral RNA detection method based on the combined use of trans-acting ribozymes and HCR-FRET analyses.PLoS One. 2024 Sep 26;19(9):e0310171. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0310171. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 39325749 Free PMC article.
-
Review of COVID-19 testing and diagnostic methods.Talanta. 2022 Jul 1;244:123409. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123409. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Talanta. 2022. PMID: 35390680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toward a next-generation diagnostic tool: A review on emerging isothermal nucleic acid amplification techniques for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 and other infectious viruses.Anal Chim Acta. 2022 May 29;1209:339338. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2021.339338. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Anal Chim Acta. 2022. PMID: 35569864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 Molecular Diagnostics in China.Clin Lab Med. 2022 Jun;42(2):193-201. doi: 10.1016/j.cll.2022.03.003. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Clin Lab Med. 2022. PMID: 35636821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SARS-CoV-2 detection using quantum dot fluorescence immunochromatography combined with isothermal amplification and CRISPR/Cas13a.Biosens Bioelectron. 2022 Apr 15;202:113978. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2022.113978. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Biosens Bioelectron. 2022. PMID: 35086029 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

