Toll-like receptor involvement in adolescent scoliotic facet joint degeneration
- PMID: 32853438
- PMCID: PMC7576299
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15733
Toll-like receptor involvement in adolescent scoliotic facet joint degeneration
Abstract
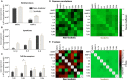
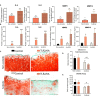
Facet joint osteoarthritis is prevalent in young patients with adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) and might contribute to back pain. Toll-like receptors (TLR) have been linked to cartilaginous tissue degeneration but their involvement in facet joint osteoarthritis in AIS patients is still unknown. We compared baseline gene expression levels of TLRs -1, -2, -4, and -6 in scoliotic and non-scoliotic chondrocytes and found higher expression levels in scoliotic chondrocytes with significantly higher TLR2 levels. Furthermore, TLR expression correlated strongly and significantly with inflammatory and catabolic markers in scoliotic but not in non-scoliotic chondrocytes. TLR activation with a synthetic TLR2/6 agonist resulted in a robust induction and release of pro-inflammatory and catabolic factors which exacerbated proteoglycan loss in scoliotic but not in non-scoliotic cartilage. We also detected a higher abundance of alarmins including S100A8/9 and biglycan in scoliotic cartilage. Finally, the small-molecule antagonists Sparstolonin B and o-Vanillin reduced catabolism following induction with naturally occurring alarmins and the synthetic TLR2/6 agonist. The high baseline expression, robust responsiveness and strong and significant correlation with proteases and pro-inflammatory cytokines suggest that TLRs are key regulators of facet joint degeneration in AIS. Blocking their activity could therefore potentially modify disease progression.
Keywords: adolescent idiopathic scoliosis; cartilage; cytokines; extracellular matrix; facet joint; metalloproteases; osteoarthritis.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to disclose. Dr Lisbet Haglund and Dr Jean Ouellet were jointly awarded a grant from the Shriners Hospitals for Children (Montreal, Canada) to perform the studies.
Figures



References
-
- Dunlop RB, Adams MA, Hutton WC. Disc space narrowing and the lumbar facet joints. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1984;66‐B:706‐710. - PubMed
-
- Adams MA, Hutton WC. The mechanical function of the lumbar apophyseal joints. Spine. 1983;8:327‐330. - PubMed
-
- Stokes IAF. Mechanical function of facet joints in the lumbar spine. Clin Biomech. 1988;3:101‐105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

