Expression of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry genes, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2, in the placenta across gestation and at the maternal-fetal interface in pregnancies complicated by preterm birth or preeclampsia
- PMID: 32853537
- PMCID: PMC7445125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.08.055
Expression of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry genes, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2, in the placenta across gestation and at the maternal-fetal interface in pregnancies complicated by preterm birth or preeclampsia
Abstract
Background: Although there is some evidence that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 can invade the human placenta, limited data exist on the gestational age-dependent expression profile of the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry mediators, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2, at the human maternal-fetal interface. There is also no information as to whether the expression of these mediators is altered in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia or preterm birth. This is important because the expression of decidual and placental angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2 across gestation may affect the susceptibility of pregnancies to vertical transmission of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2.
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the expression pattern of specific severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry genes, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2, in the placenta across human pregnancy and in paired samples of decidua and placenta in pregnancies complicated by preterm birth or preeclampsia compared with those in term uncomplicated pregnancies.
Study design: In this study, 2 separate cohorts of patients, totaling 87 pregnancies, were included. The first cohort was composed of placentae from first- (7-9 weeks), second- (16-18 weeks), and third-trimester preterm (26-31 weeks) and third-trimester term (38-41 weeks) pregnancies (n=5/group), whereas the second independent cohort included matched decidua and placentae from pregnancies from term uncomplicated pregnancies (37-41 weeks' gestation; n=14) and pregnancies complicated by preterm birth (26-37 weeks' gestation; n=11) or preeclampsia (25-37 weeks' gestation; n=42). Samples were subjected to quantitative polymerase chain reaction and next-generation sequencing or RNA sequencing for next-generation RNA sequencing for angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2 mRNA expression quantification, respectively.
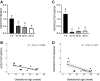
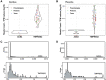
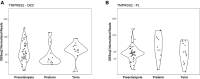
Results: In the first cohort, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2, exhibited a gestational age-dependent expression profile, that is, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and transmembrane protease serine 2 mRNA was higher (P<.05) in the first-trimester placenta than in second-trimester, preterm birth, and term placentae (P<.05) and exhibited a negative correlation with gestational age (P<.05). In the second cohort, RNA sequencing demonstrated very low or undetectable expression levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in preterm birth, preeclampsia, and term decidua and in placentae from late gestation. In contrast, transmembrane protease serine 2 was expressed in both decidual and placental samples but did not change in pregnancies complicated by either preterm birth or preeclampsia.
Conclusion: The increased expression of these severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 cell entry-associated genes in the placenta in the first trimester of pregnancy compared with those in later stages of pregnancy suggests the possibility of differential susceptibility to placental entry to severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 across pregnancy. Even though there is some evidence of increased rates of preterm birth associated with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, we found no increase in mRNA expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 or transmembrane protease serine 2 at the maternal-fetal interface.
Keywords: angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; coronavirus disease 2019; decidua; gestation age–dependent gene expression; placenta; preeclampsia; preterm birth; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; term pregnancies.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of Maternal and Neonatal SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load, Transplacental Antibody Transfer, and Placental Pathology in Pregnancies During the COVID-19 Pandemic.JAMA Netw Open. 2020 Dec 1;3(12):e2030455. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.30455. JAMA Netw Open. 2020. PMID: 33351086 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia modifies levels of the SARS-CoV-2 cell entry proteins, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2, and furin in fetal human brain endothelial cells.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023 Oct;5(10):101126. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2023.101126. Epub 2023 Aug 8. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2023. PMID: 37562534
-
Single-cell RNA expression profiling of SARS-CoV-2-related ACE2 and TMPRSS2 in human trophectoderm and placenta.Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021 Feb;57(2):248-256. doi: 10.1002/uog.22186. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2021. PMID: 32851697 Free PMC article.
-
Outcome of coronavirus spectrum infections (SARS, MERS, COVID-19) during pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 May;2(2):100107. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020. PMID: 32292902 Free PMC article.
-
Role of ACE2 in pregnancy and potential implications for COVID-19 susceptibility.Clin Sci (Lond). 2021 Aug 13;135(15):1805-1824. doi: 10.1042/CS20210284. Clin Sci (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34338772 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A review of the main placenta histopathological findings reported in coronavirus disease 2019.J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2022 Apr;17(2):165-173. doi: 10.1016/j.jtumed.2022.02.009. Epub 2022 Feb 25. J Taibah Univ Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35250425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive molecular expression profiling of SARS-CoV-associated factors in the endometrium across the menstrual cycle and elevated susceptibility in women with recurrent pregnancy loss.Front Genet. 2023 Oct 3;14:1246725. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1246725. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37854057 Free PMC article.
-
SARS- CoV-2 infection and oxidative stress in early-onset preeclampsia.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Mar 1;1868(3):166321. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166321. Epub 2021 Dec 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022. PMID: 34920081 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coronavirus Disease-2019 in Pregnancy.Clin Chest Med. 2023 Jun;44(2):373-384. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2022.11.015. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Clin Chest Med. 2023. PMID: 37085226 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 detected in placentas of 2 coronavirus disease 2019-positive asymptomatic pregnant women-case report.AJOG Glob Rep. 2021 Feb;1(1):100001. doi: 10.1016/j.xagr.2020.100001. Epub 2021 Jan 27. AJOG Glob Rep. 2021. PMID: 33842905 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

