Coronavirus RNA Proofreading: Molecular Basis and Therapeutic Targeting
- PMID: 32853546
- PMCID: PMC7402271
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.07.027
Coronavirus RNA Proofreading: Molecular Basis and Therapeutic Targeting
Erratum in
-
Coronavirus RNA Proofreading: Molecular Basis and Therapeutic Targeting.Mol Cell. 2020 Dec 17;80(6):1136-1138. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.048. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 33338403 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
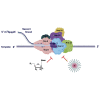
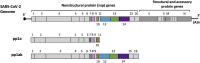
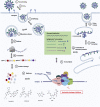
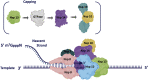
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that is wreaking havoc on worldwide public health and economies has heightened awareness about the lack of effective antiviral treatments for human coronaviruses (CoVs). Many current antivirals, notably nucleoside analogs (NAs), exert their effect by incorporation into viral genomes and subsequent disruption of viral replication and fidelity. The development of anti-CoV drugs has long been hindered by the capacity of CoVs to proofread and remove mismatched nucleotides during genome replication and transcription. Here, we review the molecular basis of the CoV proofreading complex and evaluate its potential as a drug target. We also consider existing nucleoside analogs and novel genomic techniques as potential anti-CoV therapeutics that could be used individually or in combination to target the proofreading mechanism.
Keywords: ASO; CoV; ExoN; NA; anti-coronavirus drugs; antisense oligonucleotide; coronavirus; exonuclease; non-structural protein 14; nsp14; nucleoside analog.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Agostini M.L., Andres E.L., Sims A.C., Graham R.L., Sheahan T.P., Lu X., Smith E.C., Case J.B., Feng J.Y., Jordan R., et al. Coronavirus Susceptibility to the Antiviral Remdesivir (GS-5734) Is Mediated by the Viral Polymerase and the Proofreading Exoribonuclease. MBio. 2018;9 doi: 10.1128/mBio.00221-18. Published online March 6, 2018. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agostini M.L., Pruijssers A.J., Chappell J.D., Gribble J., Lu X., Andres E.L., Bluemling G.R., Lockwood M.A., Sheahan T.P., Sims A.C., et al. Small-Molecule Antiviral β-d-N4-Hydroxycytidine Inhibits a Proofreading-Intact Coronavirus with a High Genetic Barrier to Resistance. J. Virol. 2019;93 doi: 10.1128/JVI.01348-19. Published online November 26, 2019. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almeida J.D., Berry D.M., Cunningham C.H., Hamre D., Hofstad M.S., Mallucci L., McIntosh K., Tyrrell D.A.J. Virology: Coronaviruses. Nature. 1968;220:650. 650.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

