An initial report from the French SOT COVID Registry suggests high mortality due to COVID-19 in recipients of kidney transplants
- PMID: 32853631
- PMCID: PMC7444636
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.08.005
An initial report from the French SOT COVID Registry suggests high mortality due to COVID-19 in recipients of kidney transplants
Abstract
Notwithstanding the ongoing coronavirus disease-2019 (Covid-19) pandemic, information on its clinical presentation and prognosis in recipients of a kidney transplant remain scanty. The aim of this registry-based observational study was to explore characteristics and clinical outcomes of recipients of kidney transplants included in the French nationwide Registry of Solid Organ Transplant Recipients with Covid-19. Covid-19 was diagnosed in symptomatic patients who had a positive PCR assay for SARS-CoV-2 or having typical lung lesions on imaging. Clinical and laboratory characteristics, management of immunosuppression, treatment for Covid-19, and clinical outcomes (hospitalization, admission to intensive care unit, mechanical ventilation, or death) were recorded. Risk factors for severe disease or death were determined. Of the 279 patients, 243 were admitted to hospital and 36 were managed at home. The median age of hospitalized patients was 61.6 years; most had comorbidities (hypertension, 90.1%; overweight, 63.8%; diabetes, 41.3%; cardiovascular disease, 36.2%). Fever, cough, dyspnea, and diarrhea were the most common symptoms on admission. Laboratory findings revealed mild inflammation frequently accompanied by lymphopenia. Immunosuppressive drugs were generally withdrawn (calcineurin inhibitors: 28.7%; antimetabolites: 70.8%). Treatment was mainly based on hydroxychloroquine (24.7%), antiviral drugs (7.8%), and tocilizumab (5.3%). Severe Covid-19 occurred in 106 patients (46%). Forty-three hospitalized patients died (30-day mortality 22.8%). Multivariable analysis identified overweight, fever, and dyspnea as independent risk factors for severe disease, whereas age over 60 years, cardiovascular disease, and dyspnea were independently associated with mortality. Thus, Covid-19 in recipients of kidney transplants portends a high mortality rate. Proper management of immunosuppression and tailored treatment of this population remain challenging.
Keywords: COVID-19; immunosuppression; kidney transplantation; mortality; prognosis.
Copyright © 2020 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
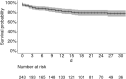


Comment in
-
The authors reply.Kidney Int. 2020 Dec;98(6):1618-1619. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.018. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 33065130 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Registry reports in COVID-19 patients: juggling with big data, poor data, and no data.Kidney Int. 2020 Dec;98(6):1618. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.09.017. Epub 2020 Oct 13. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 33065132 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

