Automated segmentation of the hypothalamus and associated subunits in brain MRI
- PMID: 32853816
- PMCID: PMC8417769
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2020.117287
Automated segmentation of the hypothalamus and associated subunits in brain MRI
Abstract
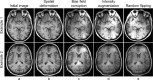
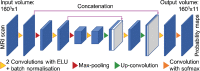
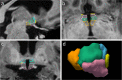
Despite the crucial role of the hypothalamus in the regulation of the human body, neuroimaging studies of this structure and its nuclei are scarce. Such scarcity partially stems from the lack of automated segmentation tools, since manual delineation suffers from scalability and reproducibility issues. Due to the small size of the hypothalamus and the lack of image contrast in its vicinity, automated segmentation is difficult and has been long neglected by widespread neuroimaging packages like FreeSurfer or FSL. Nonetheless, recent advances in deep machine learning are enabling us to tackle difficult segmentation problems with high accuracy. In this paper we present a fully automated tool based on a deep convolutional neural network, for the segmentation of the whole hypothalamus and its subregions from T1-weighted MRI scans. We use aggressive data augmentation in order to make the model robust to T1-weighted MR scans from a wide array of different sources, without any need for preprocessing. We rigorously assess the performance of the presented tool through extensive analyses, including: inter- and intra-rater variability experiments between human observers; comparison of our tool with manual segmentation; comparison with an automated method based on multi-atlas segmentation; assessment of robustness by quality control analysis of a larger, heterogeneous dataset (ADNI); and indirect evaluation with a volumetric study performed on ADNI. The presented model outperforms multi-atlas segmentation scores as well as inter-rater accuracy level, and approaches intra-rater precision. Our method does not require any preprocessing and runs in less than a second on a GPU, and approximately 10 seconds on a CPU. The source code as well as the trained model are publicly available at https://github.com/BBillot/hypothalamus_seg, and will also be distributed with FreeSurfer.
Keywords: Convolutional neural network; Hypothalamus; Public software; Segmentation.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
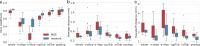
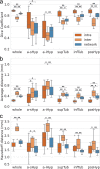
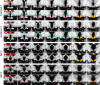
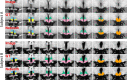
Similar articles
-
Fully Automated Hippocampus Segmentation using T2-informed Deep Convolutional Neural Networks.Neuroimage. 2024 Sep;298:120767. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120767. Epub 2024 Aug 3. Neuroimage. 2024. PMID: 39103064
-
Multi-atlas segmentation of the whole hippocampus and subfields using multiple automatically generated templates.Neuroimage. 2014 Nov 1;101:494-512. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.04.054. Epub 2014 Apr 29. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24784800
-
Multi-atlas tool for automated segmentation of brain gray matter nuclei and quantification of their magnetic susceptibility.Neuroimage. 2019 May 1;191:337-349. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.02.016. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 30738207 Free PMC article.
-
Quantifying deep grey matter atrophy using automated segmentation approaches: A systematic review of structural MRI studies.Neuroimage. 2019 Nov 1;201:116018. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116018. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Neuroimage. 2019. PMID: 31319182
-
3D fully convolutional networks for subcortical segmentation in MRI: A large-scale study.Neuroimage. 2018 Apr 15;170:456-470. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.039. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 28450139 Review.
Cited by
-
White adipose tissue distribution and amount are associated with increased white matter connectivity.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Apr;45(5):e26654. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26654. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38520361 Free PMC article.
-
Therapies to Restore Consciousness in Patients with Severe Brain Injuries: A Gap Analysis and Future Directions.Neurocrit Care. 2021 Jul;35(Suppl 1):68-85. doi: 10.1007/s12028-021-01227-y. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Neurocrit Care. 2021. PMID: 34236624 Free PMC article.
-
Segmenting hypothalamic subunits in human newborn magnetic resonance imaging data.Hum Brain Mapp. 2024 Feb 1;45(2):e26582. doi: 10.1002/hbm.26582. Hum Brain Mapp. 2024. PMID: 38339904 Free PMC article.
-
Subregional analysis of the amygdala, thalamus, and hypothalamus at the pre-decline stage in Parkinson's disease with later cognitive impairment.Front Aging Neurosci. 2025 May 9;17:1588027. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2025.1588027. eCollection 2025. Front Aging Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40416735 Free PMC article.
-
Priorities for research on neuromodulatory subcortical systems in Alzheimer's disease: Position paper from the NSS PIA of ISTAART.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 May;19(5):2182-2196. doi: 10.1002/alz.12937. Epub 2023 Jan 15. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 36642985 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abadi M., Barham P., Chen J., Chen Z., Davis A., Dean J., Devin M., Ghemawat S., Irving G., Isard M., Kudlur M., Levenberg J., Moore S., Murray D., Steiner B., Tucker P., Vasudevan V., Warden P., Wicke M., Yu Y., Zheng X. 2016. TensorFlow: a system for large-scale machine learning; pp. 265–283.
-
- Arsigny V., Commowick O., Pennec X., Ayache N. Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer; 2006. A log-euclidean framework for statistics on diffeomorphisms; pp. 924–931. - PubMed
-
- Artaechevarria X., Munoz-Barrutia A., Ortiz-de Solorzano C. Combination strategies in multi-atlas image segmentation: application to brain MR data. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging. 2009;28(8):1266–1277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

