Intrinsic disorder perspective of an interplay between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and SARS-CoV-2
- PMID: 32853823
- PMCID: PMC7444473
- DOI: 10.1016/j.meegid.2020.104510
Intrinsic disorder perspective of an interplay between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and SARS-CoV-2
Abstract
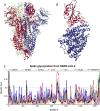
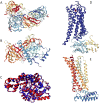
The novel severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 walks the planet causing the rapid spread of the CoV disease 2019 (COVID-19) that has especially deleterious consequences for the patients with underlying cardiovascular diseases (CVDs). Entry of the SARS-CoV-2 into the host cell involves interaction of the virus (via the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of its spike glycoprotein) with the membrane-bound form of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) followed by the virus-ACE2 complex internalization by the cell. Since ACE2 is expressed in various tissues, such as brain, gut, heart, kidney, and lung, and since these organs represent obvious targets for the SARS-CoV-2 infection, therapeutic approaches were developed to either inhibit ACE2 or reduce its expression as a means of prevention of the virus entry into the corresponding host cells. The problem here is that in addition to be a receptor for the SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells, ACE2 acts as a key component of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) aimed at the generation of a cascade of vasoactive peptides coordinating several physiological processes. In RAAS, ACE2 degrades angiotensin II, which is a multifunctional CVD-promoting peptide hormone and converts it to a heptapeptide angiotensin-(1-7) acting as the angiotensin II antagonist. As protein multifunctionality is commonly associated with the presence of flexible or disordered regions, we analyze here the intrinsic disorder predisposition of major players related to the SARS-CoV-2 - RAAS axis. We show that all considered proteins contain intrinsically disordered regions that might have specific functions. Since intrinsic disorder might play a role in the functionality of query proteins and be related to the COVID-19 pathogenesis, this work represents an important disorder-based outlook of an interplay between the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and SARS-CoV-2. It also suggests that consideration of the intrinsic disorder phenomenon should be added to the modern arsenal of means for drug development.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Afar D.E., Vivanco I., Hubert R.S., Kuo J., Chen E., Saffran D.C., Raitano A.B., Jakobovits A. Catalytic cleavage of the androgen-regulated TMPRSS2 protease results in its secretion by prostate and prostate cancer epithelia. Cancer Res. 2001;61:1686–1692. - PubMed
-
- Anthony C.S., Corradi H.R., Schwager S.L., Redelinghuys P., Georgiadis D., Dive V., Acharya K.R., Sturrock E.D. The N domain of human angiotensin-I-converting enzyme: the role of N-glycosylation and the crystal structure in complex with an N domain-specific phosphinic inhibitor, RXP407. J. Biol. Chem. 2010;285:35685–35693. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

