CAR-NK cells: A promising cellular immunotherapy for cancer
- PMID: 32853984
- PMCID: PMC7452675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102975
CAR-NK cells: A promising cellular immunotherapy for cancer
Abstract
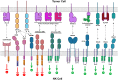
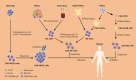
Natural Killer (NK) cells and CD8+ cytotoxic T cells are two types of immune cells that can kill target cells through similar cytotoxic mechanisms. With the remarkable success of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-engineered T (CAR-T) cells for treating haematological malignancies, there is a rapid growing interest in developing CAR-engineered NK (CAR-NK) cells for cancer therapy. Compared to CAR-T cells, CAR-NK cells could offer some significant advantages, including: (1) better safety, such as a lack or minimal cytokine release syndrome and neurotoxicity in autologous setting and graft-versus-host disease in allogenic setting, (2) multiple mechanisms for activating cytotoxic activity, and (3) high feasibility for 'off-the-shelf' manufacturing. CAR-NK cells could be engineered to target diverse antigens, enhance proliferation and persistence in vivo, increase infiltration into solid tumours, overcome resistant tumour microenvironment, and ultimately achieve an effective anti-tumour response. In this review, we focus on recent progress in genetic engineering and clinical application of CAR-NK cells, and discuss current challenges and future promise of CAR-NK cells as a novel cellular immunotherapy in cancer.
Keywords: Cancer; Chimeric antigen receptor; Immunotherapy; NK cells.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing interest All of authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Herberman RB, Nunn ME, Holden HT, Lavrin DH. Natural cytotoxic reactivity of mouse lymphoid cells against syngeneic and allogeneic tumours. II. characterization of effector cells. Int J Cancer. 1975;16(2):230–239. - PubMed
-
- Kiessling R, Klein E, Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukaemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975;5(2):112–117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

