A mouse-adapted model of SARS-CoV-2 to test COVID-19 countermeasures
- PMID: 32854108
- PMCID: PMC8034761
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2708-8
A mouse-adapted model of SARS-CoV-2 to test COVID-19 countermeasures
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: A mouse-adapted model of SARS-CoV-2 to test COVID-19 countermeasures.Nature. 2021 Feb;590(7844):E22. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03107-5. Nature. 2021. PMID: 33469219 No abstract available.
Abstract
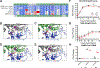
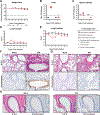
Coronaviruses are prone to transmission to new host species, as recently demonstrated by the spread to humans of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic1. Small animal models that recapitulate SARS-CoV-2 disease are needed urgently for rapid evaluation of medical countermeasures2,3. SARS-CoV-2 cannot infect wild-type laboratory mice owing to inefficient interactions between the viral spike protein and the mouse orthologue of the human receptor, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)4. Here we used reverse genetics5 to remodel the interaction between SARS-CoV-2 spike protein and mouse ACE2 and designed mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 (SARS-CoV-2 MA), a recombinant virus that can use mouse ACE2 for entry into cells. SARS-CoV-2 MA was able to replicate in the upper and lower airways of both young adult and aged BALB/c mice. SARS-CoV-2 MA caused more severe disease in aged mice, and exhibited more clinically relevant phenotypes than those seen in Hfh4-ACE2 transgenic mice, which express human ACE2 under the control of the Hfh4 (also known as Foxj1) promoter. We demonstrate the utility of this model using vaccine-challenge studies in immune-competent mice with native expression of mouse ACE2. Finally, we show that the clinical candidate interferon-λ1a (IFN-λ1a) potently inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in primary human airway epithelial cells in vitro-both prophylactic and therapeutic administration of IFN-λ1a diminished SARS-CoV-2 replication in mice. In summary, the mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 MA model demonstrates age-related disease pathogenesis and supports the clinical use of pegylated IFN-λ1a as a treatment for human COVID-196.
Figures
Update of
-
A mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 model for the evaluation of COVID-19 medical countermeasures.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2020 May 7:2020.05.06.081497. doi: 10.1101/2020.05.06.081497. bioRxiv. 2020. Update in: Nature. 2020 Oct;586(7830):560-566. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2708-8. PMID: 32511406 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

