Access to an Electronic Health Record: A Polish National Survey
- PMID: 32854345
- PMCID: PMC7503705
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17176165
Access to an Electronic Health Record: A Polish National Survey
Abstract
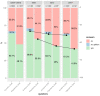
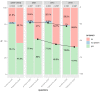
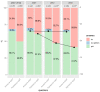
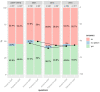
In Poland, as in many countries around the world, e-health services are becoming more and more popular. Obligatory e-sick leave was implemented, followed by e-prescriptions and e-referrals. Therefore, it is worth considering the introduction of a complete electronic health record (EHR) that can be accessed by doctors and patients. The main aim of the study is to find out whether patients want to have access to their EHRs and if they would agree to pay for such a service. The research was based on three surveys conducted among 1000 Polish adults in 2007, 2012, and 2018. The sample collection was carried out by the national opinion poll agency, with the use of computer-assisted telephone interviews. Over 60% of respondents were interested in the possibility of accessing EHRs in general, and almost 50% of them were ready to pay for it. Nevertheless, when analyzing all the year-on-year trends, they were subject to a gradual decrease. The youngest age group was the one most interested in EHRs, while the group comprising respondents in middle age was the one mostwilling to pay for it. There is still great potential in implementing EHRs on a bigger scale.
Keywords: e-health; electronic health record (EHR); national survey; telemedicine; year-on-year trends.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Usability problems do not heal by themselves: National survey on physicians' experiences with EHRs in Finland.Int J Med Inform. 2017 Jan;97:266-281. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.10.010. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Int J Med Inform. 2017. PMID: 27919385
-
Trends in the use of the Internet for health purposes in Poland.BMC Public Health. 2015 Feb 27;15:194. doi: 10.1186/s12889-015-1473-3. BMC Public Health. 2015. PMID: 25886280 Free PMC article.
-
Patient and public attitudes towards informed consent models and levels of awareness of Electronic Health Records in the UK.Int J Med Inform. 2015 Apr;84(4):237-47. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Jan 20. Int J Med Inform. 2015. PMID: 25649841 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in public perceptions of electronic health records during early years of meaningful use.Am J Manag Care. 2015 Aug;21(8):e487-93. Am J Manag Care. 2015. PMID: 26625503 Free PMC article.
-
Electronic Health Records: Then, Now, and in the Future.Yearb Med Inform. 2016 May 20;Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S48-61. doi: 10.15265/IYS-2016-s006. Yearb Med Inform. 2016. PMID: 27199197 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Knowledge, Attitudes, and Practices about Electronic Personal Health Records: A Cross-Sectional Study in a Region of Northern Italy.J Med Syst. 2024 Apr 17;48(1):42. doi: 10.1007/s10916-024-02065-z. J Med Syst. 2024. PMID: 38630322 Free PMC article.
-
User Perception of New E-Health Challenges: Implications for the Care Process.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Mar 24;19(7):3875. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19073875. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35409566 Free PMC article.
-
Inequity in the Access to eHealth and Its Decomposition Case of Poland.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Feb 18;19(4):2340. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19042340. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35206528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deetjen U. European E-Prescriptions: Benefits and Success Factors. Cyber Studies Programmme; Oxford, UK: 2016.
-
- Carnicero Giménez de Azcárate J., Rojas D. Application of Information and Communication Technologies for Health Systems in Belgium, Denmark, Spain, the United Kingdom and Sweden. Naciones Unidas, CEPAL; Santiago, Chile: 2010. Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean. Social Development Division.
-
- Hufstader M., Swain M., Furukawa M.F. State Variation in E-Prescribing Trends in the United States—ONC Data Brief. No. 4 November 2012. ONC; Washington, DC, USA: 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

