Coronaviruses: Is Sialic Acid a Gate to the Eye of Cytokine Storm? From the Entry to the Effects
- PMID: 32854433
- PMCID: PMC7564400
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9091963
Coronaviruses: Is Sialic Acid a Gate to the Eye of Cytokine Storm? From the Entry to the Effects
Abstract
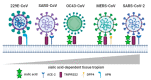
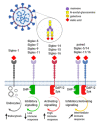
Coronaviruses (CoVs) are a diverse family of the enveloped human and animal viruses reported as causative agents for respiratory and intestinal infections. The high pathogenic potential of human CoVs, including SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, is closely related to the invasion mechanisms underlying the attachment and entry of viral particles to the host cells. There is increasing evidence that sialylated compounds of cellular glycocalyx can serve as an important factor in the mechanism of CoVs infection. Additionally, the sialic acid-mediated cross-reactivity with the host immune lectins is known to exert the immune response of different intensity in selected pathological stages. Here, we focus on the last findings in the field of glycobiology in the context of the role of sialic acid in tissue tropism, viral entry kinetics and immune regulation in the CoVs infections.
Keywords: MERS-CoV; SARS-CoV; SARS-CoV-2; Siglec; coronavirus; sialic acid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

