Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the salivary gland: immunohistochemical analysis and comparison with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32854490
- PMCID: PMC7674762
- DOI: 10.4132/jptm.2020.07.19
Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the salivary gland: immunohistochemical analysis and comparison with metastatic squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Primary squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) of the salivary gland is a rare disease, and distinguishing primary SCC from metastatic SCC is difficult. This study investigated the histological and immunohistochemical differences between primary and metastatic salivary gland SCC to improve the accuracy of diagnosis and to explore the pathogenesis of this disease.
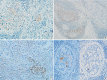
Methods: Data of 16 patients who underwent surgery for SCC of salivary glands between 2000 and 2018 at Asan Medical Center were retrieved. Eight patients had a history of SCC at other sites, and eight patients had only salivary gland SCC. Immunostaining for p16, p53, androgen receptor (AR), gross cystic disease fluid protein 15 (GCDFP-15), and c-erbB2, as well as mucicarmine staining, were compared between the two groups.
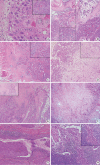
Results: Most tumors were located in the center of the salivary glands with extraparenchymal extension. The histology of primary SCC of the salivary gland was consistent with moderately differentiated SCC with extensive desmoplastic reaction and peritumoral inflammation. Involvement of the salivary gland ducts and transition into the ductal epithelium were observed in two cases. Metastatic SCC resembled the primary tumor histologically and was associated with central necrosis. Both groups exhibited negative mucin staining. Two, one, and one primary SCC case exhibited AR, GCDFP-15, and c-erbB2 positivity, respectively.
Conclusions: A subset of primary SCCs originated in salivary ducts or was related to salivary duct carcinoma. Distinguishing primary from metastatic SCC of the salivary gland is difficult using histologic features and immunoprofiles. A comprehensive review of the medical history is essential.
Keywords: Metastatic squamous cell carcinoma; Primary squamous cell carcinoma; Salivary gland.
Conflict of interest statement
J.S.S., a contributing editor of the
Figures
Similar articles
-
Expression of androgen receptor, gross cystic disease fluid protein, and CD44 in salivary duct carcinoma.Mod Pathol. 1998 Nov;11(11):1033-8. Mod Pathol. 1998. PMID: 9831198
-
Determination of the origin of oral squamous cell carcinoma by microarray analysis: Squamous epithelium or minor salivary gland?Int J Cancer. 2018 Nov 15;143(10):2551-2560. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31811. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Int J Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30121960 Free PMC article.
-
Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland.Pathol Int. 2008 May;58(5):322-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x. Pathol Int. 2008. PMID: 18429833
-
[Differential diagnosis of squamous epithelial carcinoma of the salivary glands].Pathologe. 1998 May;19(3):201-8. doi: 10.1007/s002920050274. Pathologe. 1998. PMID: 9648145 Review. German.
-
Bone marrow metastases from small cell cancer of the head and neck.Head Neck. 1994 May-Jun;16(3):266-71. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880160310. Head Neck. 1994. PMID: 8026958 Review.
Cited by
-
Morphologic CT and MRI features of primary parotid squamous cell carcinoma and its predictive factors for differential diagnosis with mucoepidermoid carcinoma.Insights Imaging. 2022 Jul 15;13(1):119. doi: 10.1186/s13244-022-01256-x. Insights Imaging. 2022. PMID: 35840821 Free PMC article.
-
Metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma accounts for nearly all squamous cell carcinomas of the parotid gland.Virchows Arch. 2024 Jul;485(1):3-11. doi: 10.1007/s00428-024-03798-5. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Virchows Arch. 2024. PMID: 38630141 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Common skin cancers and their association with other non-cutaneous primary malignancies: a review of the literature.Med Oncol. 2024 May 17;41(6):157. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02385-7. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38758457 Review.
-
Biological roles and clinical significance of estrogen and androgen receptors in head and neck cancers.J Cancer. 2022 Apr 4;13(7):2189-2199. doi: 10.7150/jca.66707. eCollection 2022. J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35517428 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pembrolizumab as a first line therapy in a patient with extensive mucoepidermoid salivary gland carcinoma. A complete clinical, radiological and pathological response. A very specific case.Discov Oncol. 2022 May 28;13(1):37. doi: 10.1007/s12672-022-00502-4. Discov Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35624380 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Batsakis JG. Primary squamous cell carcinomas of major salivary glands. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1983;92(1 Pt 1):97–8. - PubMed
-
- Chen MM, Roman SA, Sosa JA, Judson BL. Prognostic factors for squamous cell cancer of the parotid gland: an analysis of 2104 patients. Head Neck. 2015;37:1–7. - PubMed
-
- Flynn MB, Maguire S, Martinez S, Tesmer T. Primary squamous cell carcinoma of the parotid gland: the importance of correct histological diagnosis. Ann Surg Oncol. 1999;6:768–70. - PubMed
-
- Panchbhai AS. Primary squamous cell carcinoma of salivary gland: report of a rare case. J Cancer Res Ther. 2015;11:664. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

