Full-length transcriptome analysis of Phytolacca americana and its congener P. icosandra and gene expression normalization in three Phytolaccaceae species
- PMID: 32854620
- PMCID: PMC7450566
- DOI: 10.1186/s12870-020-02608-9
Full-length transcriptome analysis of Phytolacca americana and its congener P. icosandra and gene expression normalization in three Phytolaccaceae species
Abstract
Background: Phytolaccaceae species in China are not only ornamental plants but also perennial herbs that are closely related to human health. However, both large-scale full-length cDNA sequencing and reference gene validation of Phytolaccaceae members are still lacking. Therefore, single-molecule real-time sequencing technology was employed to generate full-length transcriptome in invasive Phytolacca americana and non-invasive exotic P. icosandra. Based on the transcriptome data, RT-qPCR was employed to evaluate the gene expression stability in the two plant species and another indigenous congener P. acinosa.
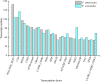
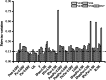
Results: Total of 19.96 Gb and 19.75 Gb clean reads of P. americana and P. icosandra were generated, including 200,857 and 208,865 full length non-chimeric (FLNC) reads, respectively. Transcript clustering analysis of FLNC reads identified 89,082 and 98,448 consensus isoforms, including 86,989 and 96,764 high-quality ones. After removing redundant reads, 46,369 and 50,220 transcripts were obtained. Based on structure analysis, total 1675 and 1908 alternative splicing variants, 25,641 and 31,800 simple sequence repeats (SSR) as well as 34,971 and 36,841 complete coding sequences were detected separately. Furthermore, 3574 and 3833 lncRNA were predicted and 41,676 and 45,050 transcripts were annotated respectively. Subsequently, seven reference genes in the two plant species and a native species P. acinosa were selected and evaluated by RT-qPCR for gene expression analysis. When tested in different tissues (leaves, stems, roots and flowers), 18S rRNA showed the highest stability in P. americana, whether infested by Spodoptera litura or not. EF2 had the most stable expression in P. icosandra, while EF1-α was the most appropriate one when attacked by S. litura. EF1-α showed the highest stability in P.acinosa, whereas GAPDH was recommended when infested by S. litura. Moreover, EF1-α was the most stable one among the three plant species whenever germinating seeds or flowers only were considered.
Conclusion: Full-length transcriptome of P. americana and P. icosandra were produced individually. Based on the transcriptome data, the expression stability of seven candidate reference genes under different experimental conditions was evaluated. These results would facilitate further exploration of functional and comparative genomic studies in Phytolaccaceae and provide insights into invasion success of P. americana.
Keywords: Full-length transcriptome analysis; Phytolaccaceae; RT-qPCR; Reference gene evaluation; SMRT sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Xiao L, Hervé MR, Carrillo J, Ding JQ, Huang W. Latitudinal trends in growth, reproduction and defense of an invasive plant. Biol Invasions. 2019;21(1):189–201. doi: 10.1007/s10530-018-1816-y. - DOI
-
- Pizzo E, Pane K, Bosso A, Landi N, Ragucci S, Russo R, et al. Novel bioactive peptides from PD-L1/2, a type 1 ribosome inactivating protein from Phytolacca dioica L. evaluation of their antimicrobial properties and anti-biofilm activities. BBA-Biomembranes. 2018;1860(7):1425–1435. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2018.04.010. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

