Comprehensive elaboration of the cGAS-STING signaling axis in cancer development and immunotherapy
- PMID: 32854711
- PMCID: PMC7450153
- DOI: 10.1186/s12943-020-01250-1
Comprehensive elaboration of the cGAS-STING signaling axis in cancer development and immunotherapy
Abstract
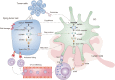
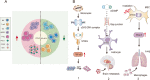
Cellular recognition of microbial DNA is an evolutionarily conserved mechanism by which the innate immune system detects pathogens. Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) and its downstream effector, stimulator of interferon genes (STING), are involved in mediating fundamental innate antimicrobial immunity by promoting the release of type I interferons (IFNs) and other inflammatory cytokines. Accumulating evidence suggests that the activation of the cGAS-STING axis is critical for antitumor immunity. The downstream cytokines regulated by cGAS-STING, especially type I IFNs, serve as bridges connecting innate immunity with adaptive immunity. Accordingly, a growing number of studies have focused on the synthesis and screening of STING pathway agonists. However, chronic STING activation may lead to a protumor phenotype in certain malignancies. Hence, the cGAS-STING signaling pathway must be orchestrated properly when STING agonists are used alone or in combination. In this review, we discuss the dichotomous roles of the cGAS-STING pathway in tumor development and the latest advances in the use of STING agonists.
Keywords: Antitumor response; Cancer development; Innate immunity; STING agonists; Type I interferon; cGAS-STING.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Akira S, Uematsu S, Takeuchi O. Pathogen recognition and innate immunity. Cell. 2006;124:783–801. - PubMed
-
- Tan X, Sun L, Chen J, Chen ZJ. Detection of microbial infections through innate immune sensing of nucleic acids. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2018;72:447–478. - PubMed
-
- Takeuchi O, Akira S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:805–820. - PubMed
-
- Hemmi H, Takeuchi O, Kawai T, Kaisho T, Sato S, Sanjo H, Matsumoto M, Hoshino K, Wagner H, Takeda K, Akira S. A toll-like receptor recognizes bacterial DNA. Nature. 2000;408:740–745. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

