Atrial Dysfunction in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 32854840
- PMCID: PMC7455760
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.07.009
Atrial Dysfunction in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
Background: Paroxysmal and permanent atrial fibrillation (AF) are common in heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Objectives: This study sought to determine the implications of left atrial (LA) myopathy and dysrhythmia across the spectrum of AF burden in HFpEF.
Methods: Consecutive patients with HFpEF (n = 285) and control subjects (n = 146) underwent invasive exercise testing and echocardiographic assessment of cardiac structure, function, and pericardial restraint.
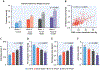
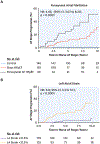
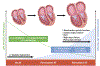
Results: Patients with HFpEF were categorized into stages of AF progression: 181 (65%) had no history of AF, 49 (18%) had paroxysmal AF, and 48 (17%) had permanent AF. Patients with permanent AF were more congested with greater pulmonary vascular disease and lower cardiac output. LA volumes increased, while LA compliance, LA reservoir strain, and right ventricular function decreased with increasing AF burden. The presence of permanent AF was characterized by a distinct pathophysiology, with greater total heart volume caused by atrial dilatation, leading to elevated filling pressures through heightened pericardial restraint. Survival decreased with increasing AF burden. Ten-year progression to permanent AF was common, particularly in paroxysmal AF (52%), and the likelihood of AF progression increased with higher AF stage, poorer LA compliance, and lower LA strain.
Conclusions: LA compliance and mechanics progressively decline with increasing AF burden in HFpEF, increasing risk for new onset AF and progressive AF. These changes promote development of a unique phenotype of HFpEF characterized by heightened ventricular interaction, right heart failure, and worsening pulmonary vascular disease. Further study is required to identify therapeutic interventions targeting LA myopathy to improve outcomes in HFpEF.
Keywords: HFpEF; atrial fibrillation; exercise hemodynamics; left atrial strain; pericardial restraint.
Copyright © 2020 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Comment in
-
Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction and Atrial Fibrillation: How to Fight Allied Enemies.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020 Sep 1;76(9):1065-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2020.07.024. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32854841 No abstract available.
References
-
- Zafrir B, Lund LH, Laroche C, et al. Prognostic implications of atrial fibrillation in heart failure with reduced, mid-range, and preserved ejection fraction: a report from 14 964 patients in the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur Heart J 2018;39: 4277–84. - PubMed
-
- Kotecha D, Lam CS, Van Veldhuisen DJ, Van Gelder IC, Voors AA, Rienstra M. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction and atrial fibrillation: vicious twins. J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;68:2217–28. - PubMed
-
- Melenovsky V, Borlaug BA, Rosen B, et al. Cardiovascular features of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction versus nonfailing hypertensive left ventricular hypertrophy in the urban Baltimore community: the role of atrial remodeling/dysfunction. J Am Coll Cardiol 2007;49: 198–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

