Loss of SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Alters NRF2 Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
- PMID: 32855269
- PMCID: PMC7718321
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0082
Loss of SWI/SNF Chromatin Remodeling Alters NRF2 Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
Abstract
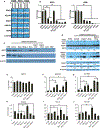
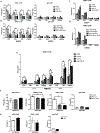
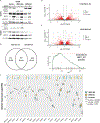
The NF-E2-related factor 2 (referred to as NRF2) transcription factor binds antioxidant responsive elements within the promoters of cytoprotective genes to induce their expression. Next-generation sequencing studies in lung cancer have shown a significant number of activating mutations within the NRF2 signaling pathway. Mutations in components of the SWI/SNF chromatin-remodeling complex, a general regulator of transcription using either BRG1 or BRM as the catalytic subunit, also frequently occur in lung cancers. Importantly, low BRG1 expression levels in primary human NSCLC correlated with increased NRF2-target gene expression. Here, we show that loss of SWI/SNF complex function activated a subset of NRF2-mediated transcriptional targets. Using a series of isogenic NSCLC lines with reduced or depleted BRG1 and/or BRM expression, we observed significantly increased expression of the NRF2-target genes HMOX1 and GSTM4. In contrast, expression of the NRF2 target genes NQO1 and GCLM modestly increased following BRM reduction. Chromatin immunoprecipitation showed that BRG1 knockdown led to increased NRF2 binding at its respective ARE sites in the HMOX1 promoter but not in NQO1 and GCLM. Our data demonstrate that loss of BRG1 or BRM in lung cancer results in activation of the NRF2/KEAP1 pathway and HMOX1 expression. Therefore, we provide an additional molecular explanation for why patients harboring BRG1 or BRM mutations show poor prognoses. A better understanding of this mechanism may yield novel insights into the design of targeted treatment modalities. IMPLICATIONS: Our study identifies a novel mechanism for how mutations in the SMARCA4 gene may drive progression of human lung adenocarcinomas.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not declare any conflicts of interests.
Figures
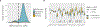

Similar articles
-
BRG1 interacts with Nrf2 to selectively mediate HO-1 induction in response to oxidative stress.Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Nov;26(21):7942-52. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00700-06. Epub 2006 Aug 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16923960 Free PMC article.
-
Brg1-mediated Nrf2/HO-1 pathway activation alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Jun 1;8(6):e2841. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.236. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28569786 Free PMC article.
-
A synthetic lethality-based strategy to treat cancers harboring a genetic deficiency in the chromatin remodeling factor BRG1.Cancer Res. 2013 Sep 1;73(17):5508-18. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4593. Epub 2013 Jul 19. Cancer Res. 2013. PMID: 23872584
-
SMARCA4/BRG1-Deficient Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas: A Case Series and Review of the Literature.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021 Jan 1;145(1):90-98. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0633-OA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2021. PMID: 33367658 Review.
-
Involvement of the chromatin-remodeling factor BRG1/SMARCA4 in human cancer.Epigenetics. 2008 Mar-Apr;3(2):64-8. doi: 10.4161/epi.3.2.6153. Epub 2008 Apr 17. Epigenetics. 2008. PMID: 18437052 Review.
Cited by
-
The roles of inducible chromatin and transcriptional memory in cellular defense system responses to redox-active pollutants.Free Radic Biol Med. 2021 Jul;170:85-108. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2021.03.018. Epub 2021 Mar 28. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 33789123 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metabolic reprogramming by histone deacetylase inhibition preferentially targets NRF2-activated tumors.Cell Rep. 2024 Jan 23;43(1):113629. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113629. Epub 2023 Dec 30. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38165806 Free PMC article.
-
Re-expression of SMARCA4/BRG1 in small cell carcinoma of ovary, hypercalcemic type (SCCOHT) promotes an epithelial-like gene signature through an AP-1-dependent mechanism.Elife. 2020 Dec 23;9:e59073. doi: 10.7554/eLife.59073. Elife. 2020. PMID: 33355532 Free PMC article.
-
A narrative review of prognosis prediction models for non-small cell lung cancer: what kind of predictors should be selected and how to improve models?Ann Transl Med. 2021 Oct;9(20):1597. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-4733. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34790803 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ARID1A loss is associated with increased NRF2 signaling in human head and neck squamous cell carcinomas.PLoS One. 2024 Feb 15;19(2):e0297741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0297741. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38358974 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

