Increased IgE-Mediated Food Allergy With Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis
- PMID: 32855350
- PMCID: PMC8323611
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2020-0202
Increased IgE-Mediated Food Allergy With Food Protein-Induced Allergic Proctocolitis
Conflict of interest statement
POTENTIAL CONFLICT OF INTEREST: The authors have indicated they have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
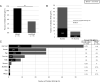
Figures
References
-
- Jones SM, Burks AW. Food allergy. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(12):1168–1176 - PubMed
-
- lerodiakonou D, Garcia-Larsen V, Logan A, et al. . Timing of allergenic food introduction to the infant diet and risk of allergic or autoimmune disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA. 2016;316(11):1181–1192 - PubMed
-
- Odze RD, Wershil BK, Leichtner AM, Antonioli DA. Allergic colitis in infants. J Pediatr. 1995;126(2):163–170 - PubMed
-
- Høst A, Halken S, Jacobsen HP, Christensen AE, Herskind AM, Plesner K. Clinical course of cow’s milk protein allergy/intolerance and atopic diseases in childhood. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2002;13(s15):23–28 - PubMed
-
- Venter C, Brown T, Meyer R, et al. . Better recognition, diagnosis and management of non-IgE-mediated cow’s milk allergy in infancy: iMAP-an international interpretation of the MAP (Milk Allergy in Primary Care) guideline. [published correction appears in Clin Transl Allergy. 2018;4:4]. Clin Transl Allergy. 2017;7(1):26. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

