IL-21 mediates microRNA-423-5p /claudin-5 signal pathway and intestinal barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease
- PMID: 32855360
- PMCID: PMC7485739
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103566
IL-21 mediates microRNA-423-5p /claudin-5 signal pathway and intestinal barrier function in inflammatory bowel disease
Abstract
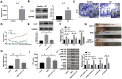
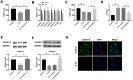
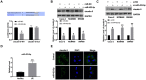
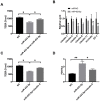
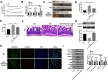
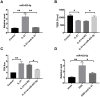
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of chronic and recurrent nonspecific inflammatory disorders, including Crohn's disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). Due to the persistent inflammation of intestinal mucosa caused by immune disorders, barrier dysfunction may be an essential cause of the pathogenesis of IBD. Therefore, exploring the mechanism is very important to clarify the pathogenesis of IBD. In our research, we provided evidence of IL-21 function in IBD. The junction complex protein claudin-5 may be a downstream gene of the IL-21. Anti-IL-21 administrated prevented DSS-simulative colitis via recovering claudin-5 expression in the human colonic epithelial cells. Meanwhile, we described that miR-423-5p could be involved in IL-21/ claudin-5 pathway by regulating NF-κB/MAPKs/JNK signaling pathway, which may provide a new therapeutic target for IBD.
Keywords: IBD; IL-21; claudin-5; inflammation; microRNA-423-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA 301A Promotes Intestinal Inflammation and Colitis-Associated Cancer Development by Inhibiting BTG1.Gastroenterology. 2017 May;152(6):1434-1448.e15. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.049. Epub 2017 Feb 11. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28193514
-
Deficiency of microRNA-10b promotes DSS-induced inflammatory response via impairing intestinal barrier function.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022 Dec 25;636(Pt 2):48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.10.096. Epub 2022 Oct 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2022. PMID: 36343490
-
Long Non-coding RNA MEG3 Alleviated Ulcerative Colitis Through Upregulating miR-98-5p-Sponged IL-10.Inflammation. 2021 Jun;44(3):1049-1059. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01400-z. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Inflammation. 2021. PMID: 33394187
-
Development, validation and implementation of an in vitro model for the study of metabolic and immune function in normal and inflamed human colonic epithelium.Dan Med J. 2015 Jan;62(1):B4973. Dan Med J. 2015. PMID: 25557335 Review.
-
CXCL8 chemokine in ulcerative colitis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2021 Jun;138:111427. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111427. Epub 2021 Mar 8. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 33706134 Review.
Cited by
-
Super Carbonate Apatite-miR-497a-5p Complex Is a Promising Therapeutic Option against Inflammatory Bowel Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 19;16(4):618. doi: 10.3390/ph16040618. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111375 Free PMC article.
-
Updated immunomodulatory roles of gut flora and microRNAs in inflammatory bowel diseases.Clin Exp Med. 2023 Aug;23(4):1015-1031. doi: 10.1007/s10238-022-00935-9. Epub 2022 Nov 16. Clin Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36385416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ethanolic extract of domesticated Amauroderma rugosum alleviated DSS-induced ulcerative colitis via repairing the intestinal barrier.Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024 Apr 18;33(14):3335-3345. doi: 10.1007/s10068-024-01565-5. eCollection 2024 Nov. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39328223 Free PMC article.
-
Main genetic factors associated with inflammatory bowel diseases and their consequences on intestinal permeability: involvement in gut inflammation.J Gastroenterol. 2025 Aug 21. doi: 10.1007/s00535-025-02289-x. Online ahead of print. J Gastroenterol. 2025. PMID: 40841786 Review.
-
Circulating miRNA Profile in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients with Stress, Anxiety, and Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 29;26(15):7321. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157321. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806453 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Laube R, Yau Y, Selinger CP, Seow CH, Thomas A, Wei Chuah S, Hilmi I, Mao R, Ong D, Ng SC, Wei SC, Banerjee R, Ahuja V, et al.. Knowledge and attitudes towards pregnancy in females with inflammatory bowel disease - an international, multi-centre study. J Crohns Colitis. 2020. [Epub ahead of print]. 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa047 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Wu JC, Chan FK, Sung JJ, Kaplan GG. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2018; 390:2769–78. 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32448-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Faghih M, Rostami-Nejad M, Amani D, Sadeghi A, Pourhoseingholi MA, Masotti A, Zali MR. Analysis of IL17A and IL21 expression in the small intestine of celiac disease patients and correlation with circulating thioredoxin level. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 2018; 22:518–25. 10.1089/gtmb.2018.0128 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Caielli S, Veiga DT, Balasubramanian P, Athale S, Domic B, Murat E, Banchereau R, Xu Z, Chandra M, Chung CH, Walters L, Baisch J, Wright T, et al.. A CD4+ T cell population expanded in lupus blood provides B cell help through interleukin-10 and succinate. Nat Med. 2019; 25:75–81. 10.1038/s41591-018-0254-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

