Bilateral peritonsillar abscess: a case study and literature review
- PMID: 32855785
- PMCID: PMC7444442
- DOI: 10.1093/jscr/rjaa112
Bilateral peritonsillar abscess: a case study and literature review
Abstract
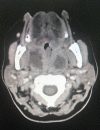
While peritonsillar abscesses are the most common deep neck infections, bilateral forms are rare. A peritonsillar abscess occurs when pus accumulates in the peritonsillar space, located between the tonsils and superior constrictor muscle, causing medial displacement of the uvula, trismus, odynophagia or even upper airway obstruction. High clinical suspicion is needed to diagnose bilateral peritonsillar abscess due to frequent history, computerized tomography scan of the neck with IV contrast facilitates accurate diagnose and a full assessment of the patient. Incision and drainage are needed to evacuate the pus along with systemic antibiotics to relieve patient symptoms followed by interval tonsillectomy, which usually done after 6 weeks.
Keywords: acute tonsillitis; bilateral; complication; peritonsillar abscess.
Published by Oxford University Press and JSCR Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved. © The Author(s) 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peritonsillar abscess: clinical aspects of microbiology, risk factors, and the association with parapharyngeal abscess.Dan Med J. 2017 Mar;64(3):B5333. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260599 Review.
-
[Bilateral peritonsillar abscess in children: case report].Arch Argent Pediatr. 2019 Jun 1;117(3):e297-e300. doi: 10.5546/aap.2019.e297. Arch Argent Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31063321 Spanish.
-
Bilateral peritonsillar abscess: A rare emergency.Malays Fam Physician. 2018 Apr 30;13(1):41-44. eCollection 2018. Malays Fam Physician. 2018. PMID: 29796210 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical practice guideline: tonsillitis II. Surgical management.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Apr;273(4):989-1009. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-3904-x. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2016. PMID: 26882912
-
Bilateral peritonsillar abscesses: case report and literature review.Am J Otolaryngol. 2006 Nov-Dec;27(6):443-5. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2006.03.010. Am J Otolaryngol. 2006. PMID: 17084235 Review.
Cited by
-
Infectious Mononucleosis Complicated with Bilateral Peritonsillar Abscess and Splenic Infarction.Case Rep Infect Dis. 2021 Mar 12;2021:6623834. doi: 10.1155/2021/6623834. eCollection 2021. Case Rep Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 33777464 Free PMC article.
-
Bilateral Peritonsillar Abscesses Subsequent to Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Case Report.Cureus. 2025 Feb 5;17(2):e78590. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78590. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40062054 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources