Isolation and characterization of a novel bacterial strain from a Tris-Acetate-Phosphate agar medium plate of the green micro-alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii that can utilize common environmental pollutants as a carbon source
- PMID: 32855811
- PMCID: PMC7425125
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.24680.1
Isolation and characterization of a novel bacterial strain from a Tris-Acetate-Phosphate agar medium plate of the green micro-alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii that can utilize common environmental pollutants as a carbon source
Abstract
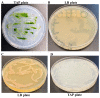
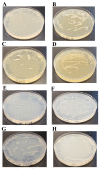
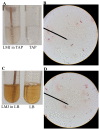
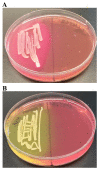
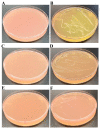
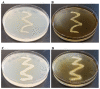
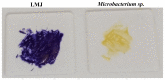
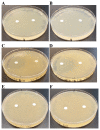
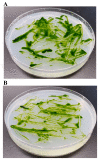
Background:Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a green micro-alga can be grown at the lab heterotrophically or photo-heterotrophically in Tris-Phosphate-Acetate (TAP) medium which contains acetate as the sole carbon source. When grown in TAP medium, Chlamydomonas can utilize the exogenous acetate in the medium for gluconeogenesis using the glyoxylate cycle, which is also present in many bacteria and higher plants. A novel bacterial strain, LMJ, was isolated from a contaminated TAP medium plate of Chlamydomonas. We present our work on the isolation and physiological and biochemical characterizations of LMJ. Methods: Several microbiological tests were conducted to characterize LMJ, including its sensitivity to four antibiotics. We amplified and sequenced partially the 16S rRNA gene of LMJ. We tested if LMJ can utilize cyclic alkanes, aromatic hydrocarbons, poly-hydroxyalkanoates, and fresh and combusted car motor oil as the sole carbon source on Tris-Phosphate (TP) agar medium plates for growth. Results: LMJ is a gram-negative rod, oxidase-positive, mesophilic, non-enteric, pigmented, salt-sensitive bacterium. LMJ can ferment glucose, is starch hydrolysis-negative, and is very sensitive to penicillin and chloramphenicol. Preliminary spectrophotometric analyses indicate LMJ produces pyomelanin. NCBI-BLAST analyses of the partial 16S rRNA gene sequence of LMJ showed that it matched to that of an uncultured bacterium clone LIB091_C05_1243. The nearest genus relative of LMJ is an Acidovorax sp. strain. LMJ was able to use alkane hydrocarbons, fresh and combusted car motor oil, poly-hydroxybutyrate, phenanthrene, naphthalene, benzoic acid and phenyl acetate as the sole carbon source for growth on TP-agar medium plates. Conclusions: LMJ has 99.14% sequence identity with the Acidovorax sp. strain A16OP12 whose genome has not been sequenced yet. LMJ's ability to use chemicals that are common environmental pollutants makes it a promising candidate for further investigation for its use in bioremediation and, provides us with an incentive to sequence its genome.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene; Acidovorax sp.; Chlamydomonas; LMJ; TAP medium; bioremediation; penicillin-sensitivity; pyomelanin.
Copyright: © 2020 Mitra M et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Isolation and characterization of a novel Sphingobium yanoikuyae strain variant that uses biohazardous saturated hydrocarbons and aromatic compounds as sole carbon sources.F1000Res. 2020 Jul 24;9:767. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.25284.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32934808 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of Acidovorax temperans strain LMJ isolated from a contaminated Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Tris-Acetate-Phosphate medium culture plate.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024 Apr 11;13(4):e0129323. doi: 10.1128/mra.01293-23. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024. PMID: 38488374 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal- and antibiotic-tolerant novel bacterial strain from a contaminated culture plate of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, a green micro-alga.F1000Res. 2021 Jul 5;10:533. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.53779.2. eCollection 2021. F1000Res. 2021. PMID: 34540203 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation of Previously Uncultured Slow-Growing Bacteria by Using a Simple Modification in the Preparation of Agar Media.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018 Sep 17;84(19):e00807-18. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00807-18. Print 2018 Oct 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30030229 Free PMC article.
-
Acetate in mixotrophic growth medium affects photosystem II in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and protects against photoinhibition.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013 Oct;1827(10):1183-90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbabio.2013.06.004. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013. PMID: 23791666
Cited by
-
Isolation and characterization of a novel Sphingobium yanoikuyae strain variant that uses biohazardous saturated hydrocarbons and aromatic compounds as sole carbon sources.F1000Res. 2020 Jul 24;9:767. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.25284.1. eCollection 2020. F1000Res. 2020. PMID: 32934808 Free PMC article.
-
Programmed cell death and redox metabolism protect Chlamydomonas reinhardtii populations from the galactic cosmic environment on the Artemis-1 mission.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 2;15(1):23396. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-05419-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40603369 Free PMC article.
-
Complete genome sequence of Acidovorax temperans strain LMJ isolated from a contaminated Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Tris-Acetate-Phosphate medium culture plate.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024 Apr 11;13(4):e0129323. doi: 10.1128/mra.01293-23. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2024. PMID: 38488374 Free PMC article.
-
Applications of the Microalgae Chlamydomonas and Its Bacterial Consortia in Detoxification and Bioproduction.Life (Basel). 2024 Jul 27;14(8):940. doi: 10.3390/life14080940. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39202682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional Response and Plant Growth Promoting Activity of Pseudomonas fluorescens DR397 under Drought Stress Conditions.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Aug 31;10(4):e0097922. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.00979-22. Epub 2022 Jul 12. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 35863006 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang H, Qiao Y, Chai B, et al. : Identification and Molecular Characterization of the Homogentisate Pathway Responsible for Pyomelanin Production, the Major Melanin Constituents in Aeromonas media WS. PLoS One.Virolle M-J, editor.2015;10(3):e0120923. 10.1371/journal.pone.0120923 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

