Clinical Application of Infrared-Light Microperimetry in the Assessment of Scotopic-Eye Sensitivity
- PMID: 32855854
- PMCID: PMC7422764
- DOI: 10.1167/tvst.9.8.7
Clinical Application of Infrared-Light Microperimetry in the Assessment of Scotopic-Eye Sensitivity
Abstract
Purpose: The eye can see pulsed near-infrared (IR) radiation with the color corresponding to half of the wavelength used. Until recently, the technology required for measuring IR vision was confined to optical laboratories and was not studied clinically. The current investigation sought to determine the values for IR thresholds in a healthy population.
Methods: IR-light threshold was measured in 45 healthy participants, aged from 21 to 70 years. Ten patients with retinal pathology were included for comparison. Ocular media clarity was assessed with a straylight parameter. The sensitivity of dark-adapted eyes (expressed on a 0-26 dB scale) were tested using an IR microperimeter. The device consists of a femtosecond laser that emits 1045 nm light to project a stimulus at the retina.
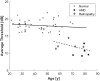
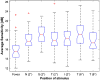
Results: All participants were able to see the IR stimulus, which they perceived as green, and all performed the test. Measurements at seven locations revealed lower sensitivity at the fovea (15.5 dB) than in paracentral regions (18.2 dB). We noted a significant straylight increase with age. Although, in our study population, it was only a slight, -0.18 dB decline per decade of the average IR-sensitivity. The retinal-pathology group demonstrated impaired sensitivity to IR light.
Conclusions: We showed that IR-light sensitivity does not significantly decrease with age despite a straylight increase. A reference level for the IR threshold was proposed. The application of IR-light microperimetry can be extended to the assessment of retinal pathology.
Translational relevance: IR-light microperimetry could be applied clinically to measure visual function.
Keywords: IR threshold; aging; scotopic sensitivity; straylight.
Copyright 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: G. Łabuz, None; A. Rayamajhi, None; J. Usinger, None; K. Komar (P); P. Merz, None; R. Khoramnia (F); G. Palczewska (P, F); K. Palczewski (F); G.U. Auffarth (F)
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fotopic and scotopic retinal sensitivity and foveal fixation normal values using microperimetry in healthy population.Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2022 Dec;97(12):684-691. doi: 10.1016/j.oftale.2022.06.014. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol (Engl Ed). 2022. PMID: 35871998
-
Blue cone monochromacy: visual function and efficacy outcome measures for clinical trials.PLoS One. 2015 Apr 24;10(4):e0125700. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125700. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25909963 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Photon Microperimetry: A Media Opacity-Independent Retinal Function Assay.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021 Feb 5;10(2):11. doi: 10.1167/tvst.10.2.11. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2021. PMID: 34003895 Free PMC article.
-
[A new approach for studying the retinal and choroidal circulation].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004 Dec;108(12):836-61; discussion 862. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2004. PMID: 15656089 Review. Japanese.
-
Scotopic microperimetry: evolution, applications and future directions.Clin Exp Optom. 2022 Nov;105(8):793-800. doi: 10.1080/08164622.2021.2023477. Epub 2022 Jan 13. Clin Exp Optom. 2022. PMID: 35025727 Review.
Cited by
-
Femtosecond Er-doped fiber laser source tunable from 872 to 1075 nm for two-photon vision studies in humans.Biomed Opt Express. 2022 Mar 4;13(4):1899-1911. doi: 10.1364/BOE.452609. eCollection 2022 Apr 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2022. PMID: 35519271 Free PMC article.
-
Two-photon microperimetry with picosecond pulses.Biomed Opt Express. 2020 Dec 17;12(1):462-479. doi: 10.1364/BOE.411168. eCollection 2021 Jan 1. Biomed Opt Express. 2020. PMID: 33659083 Free PMC article.
-
Infrared- and white-light retinal sensitivity in glaucomatous neuropathy.Sci Rep. 2022 Feb 4;12(1):1961. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-05718-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35121766 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Photon Vision in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Translational Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2022 Mar 21;12(3):760. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12030760. Diagnostics (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35328313 Free PMC article.
-
From mouse to human: Accessing the biochemistry of vision in vivo by two-photon excitation.Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023 Mar;93:101170. doi: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2023.101170. Epub 2023 Feb 12. Prog Retin Eye Res. 2023. PMID: 36787681 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Griffin DR, Hubbard R, Wald G. The sensitivity of the human eye to infra-red radiation. J Opt Soc Am. 1947; 37: 546–554. - PubMed
-
- Vos JJ. Colorimetric and photometric properties of a 2 fundamental observer. Color Res Appl. 1978; 3: 125–128.
-
- Dmitriev VG, Emel'yanov V, Kashintsev M, et al. .. Nonlinear perception of infrared radiation in the 800–1355 nm range with human eye. Soviet J Quantum Elect. 1979; 9: 475.
-
- Sliney DH, Wangemann RT, Franks JK, Wolbarsht ML. Visual sensitivity of the eye to infrared laser radiation. J Opt Soc Am. 1976; 66: 339–341. - PubMed
-
- Theodossiou T, Georgiou E, Hovhannisyan V, Yova D. Visual observation of infrared laser speckle patterns at half their fundamental wavelength. Lasers Med Sci. 2001; 16: 34–39. - PubMed

