A Novel Predictive Marker for In-Hospital Mortality in Acute Cerebral Infarction: Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to Lymphocyte Ratio
- PMID: 32855897
- PMCID: PMC7447148
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.9986
A Novel Predictive Marker for In-Hospital Mortality in Acute Cerebral Infarction: Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol to Lymphocyte Ratio
Abstract
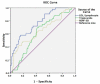
Objectives Neutrophil to eosinophil ratio, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio, C-reactive protein to albumin ratio, and red blood cell distribution width (RDW) have been studied in patients with acute cerebral infarction (ACI). However, the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) to lymphocyte ratio has never been studied. Hence, our objective was to study the LDL-C to lymphocyte ratio with regard to in-hospital mortality rates of patients with ACI. Materials and methods We retrospectively examined our patients diagnosed with ACI between January 2015 and December 2018. The patients' clinical data and imaging and laboratory results during the acute period were retrieved from our database and saved for statistical analysis. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to evaluate the predictive value of the variables and to calculate the cut-off values. Results A total of 172 patients with ACI, including 43 patients who died and 129 patients who survived in the hospital, were included in the study. The median age of the patients who died was significantly higher than that of those who survived (p: <0.001). Median triglyceride level, LDL-C to lymphocyte ratio, and RDW-SD values were significantly higher in patients who died (p = 0.017, p: <0.001, and p = 0.003, respectively). Areas under the ROC curve were found to be as follows: LDL-C to lymphocyte ratio: 0.774 (95% CI: 0.697-0.851), RDW-SD: 0.562 (95% CI: 0.456-0.669), and triglyceride level: 0.621 (95% CI: 0.531-0.732). The cut-off value of the LDL-C to lymphocyte ratio was 59.71 (sensitivity: 79.1%; specificity: 58.1%). Conclusions The LDL-C to lymphocyte ratio can be used as a marker to predict in-hospital mortality in patients with ACI. We recommend further studies to verify our findings.
Keywords: acute cerebral infarction; high density lipoprotein-cholesterol; low density lipoprotein-cholesterol; lymphocyte; red blood cell distribution width; stroke.
Copyright © 2020, Güneş et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Correlation between neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio combined with low-density lipoprotein cholesterol/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and severity of coronary artery disease in patients with acute coronary syndrome].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022 Mar;34(3):274-279. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20211008-01441. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2022. PMID: 35574745 Chinese.
-
Is neutrophil/eosinophil ratio at admission a prognostic marker for in-hospital mortality of acute ischemic stroke?J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020 Aug;29(8):104999. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2020.104999. Epub 2020 Jun 14. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2020. PMID: 32689649
-
The relationship between NLR, LDL-C/HDL-C, NHR and coronary artery disease.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 10;19(7):e0290805. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0290805. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38985788 Free PMC article.
-
Neutrophil to high-density lipoprotein ratio has a superior prognostic value in elderly patients with acute myocardial infarction: a comparison study.Lipids Health Dis. 2020 Apr 4;19(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12944-020-01238-2. Lipids Health Dis. 2020. PMID: 32247314 Free PMC article.
-
In-hospital and mid-term follow-up of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and target-goal attainment among patients with acute cerebral infarction: a retrospective study.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Feb 28;23(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02044-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 38419043 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Integrating Neutrophil-To-Albumin Ratio and Triglycerides: A Novel Indicator for Predicting Spontaneous Hemorrhagic Transformation in Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Dec;30(12):e70133. doi: 10.1111/cns.70133. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39690502 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinflammatory biomarkers as predictors of hemorrhagic transformation in acute ischemic stroke patients after endovascular thrombectomy.Front Neurol. 2025 Jun 13;16:1606563. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1606563. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40584526 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of the C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with stroke: a meta-analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 1;15(1):21150. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-07327-5. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40596569 Free PMC article.
-
The Relationship of Low-Density-Lipoprotein to Lymphocyte Ratio with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022 Sep 8;17:2175-2185. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S369161. eCollection 2022. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2022. PMID: 36106158 Free PMC article.
-
Red cell index: A novel biomarker for 3-month mortality in acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis.Brain Behav. 2021 Jun;11(6):e02170. doi: 10.1002/brb3.2170. Epub 2021 May 4. Brain Behav. 2021. PMID: 33943024 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ. Lancet. 2006;367:1747–1757. - PubMed
-
- Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd. Stroke. 1993;24:35–41. - PubMed
-
- Relationship between blood pressure levels during thrombolytic therapy and functional outcomes in patients with middle cerebral artery infarction. Güneş M. J Surg Med. 2020;4:378–382.
-
- Age and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale Score within 6 hours after onset are accurate predictors of outcome after cerebral ischemia: development and external validation of prognostic models. Weimar C, König IR, Kraywinkel K, Ziegler A, Diener HC; German Stroke Study Collaboration. Stroke. 2004;35:158–162. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials