Comparison of Blood Glucose Variability Between Exenatide and Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30 in Chinese Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin Monotherapy: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized Trial
- PMID: 32856226
- PMCID: PMC7509011
- DOI: 10.1007/s13300-020-00904-z
Comparison of Blood Glucose Variability Between Exenatide and Biphasic Insulin Aspart 30 in Chinese Participants with Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled with Metformin Monotherapy: A Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized Trial
Abstract
Introduction: To compare blood glucose variability (GV) in Chinese participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) whose blood glucose levels are inadequately controlled with metformin monotherapy after twice-daily exenatide or biphasic insulin aspart 30 (BIAsp30).
Methods: In this 16-week multicenter, randomized clinical trial, 104 participants were randomized 1:1 to receive exenatide (exenatide group) or BIAsp30 (BIAsp30 group) twice daily. All participants continued metformin treatment. The primary outcome was the change in GV as measured by a continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS) from baseline to 16 weeks.
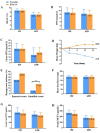
Results: At 16 weeks, both the Exenatide and BIAsp30 groups effectively decreased mean glucose (MG), but neither group changed the mean amplitude of glycemic excursion (MAGE), largest amplitude of glycemic excursion (LAGE), mean of daily difference (MODD), or standard deviation of blood glucose (SDBG). The decrease in 2-h post-breakfast glucose excursions was greater in the Exenatide group compared to the BIAsp30 group, with a least square (LS) mean difference [95% CI] of (1.58 [0.53, 2.63]). Exenatide also significantly reduced 2-h post-lunch glucose excursion compared to BIAsp30 (LS mean difference [95% CI], 1.19 [0.18, 2.20]). The Exenatide group had significantly reduced body weight and body mass index (BMI), while the BIAsp30 group had increased weight and had no change in BMI. Both treatments were well tolerated with no serious hypoglycemic events and with fewer identified hypoglycemic events in the Exenatide group than in the BIAsp30 group (5.77% vs. 17.31%, P < 0.01).
Conclusion: Although there was no difference in change of GV between Exenatide and BIAsp30, exenatide provided more improvement in postprandial glucose excursion and weight control, without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia in Chinese patients with T2DM whose blood glucose was inadequately controlled with metformin. These findings may provide new options for patients who choose further hypoglycemic treatment, especially in patients with obesity who have large postprandial plasma glucose excursions.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov indentifier: NCT02449603.
Keywords: Biphasic insulin aspart 30 (BIAsp30); Continuous glucose monitoring system (CGMS); Exenatide; Glucose variability; Postprandial glucose excursion.
Figures
References
-
- Hermansen K, Colombo M, Storgaard H, Østergaard A, Kolendorf K, Madsbad S. Improved postprandial glycemic control with biphasic insulin aspart relative to biphasic insulin lispro and biphasic human insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2002;25(5):883–888. - PubMed
-
- Yang W, Ersoy C, Wang G, Ye S, Liu J, Miao H, et al. Efficacy and safety of three-times-daily versus twice-daily biphasic insulin aspart 30 in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with basal insulin combined with oral antidiabetic drugs. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019;150:158–166. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

