Antioxidant Apigenin Relieves Age-Related Muscle Atrophy by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Hyperactive Mitophagy and Apoptosis in Skeletal Muscle of Mice
- PMID: 32857105
- PMCID: PMC7566467
- DOI: 10.1093/gerona/glaa214
Antioxidant Apigenin Relieves Age-Related Muscle Atrophy by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Hyperactive Mitophagy and Apoptosis in Skeletal Muscle of Mice
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Antioxidant Apigenin Relieves Age-Related Muscle Atrophy by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and Hyperactive Mitophagy and Apoptosis in Skeletal Muscle of Mice.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022 Jun 1;77(6):1173. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glac086. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2022. PMID: 35486377 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
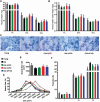
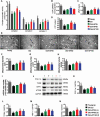
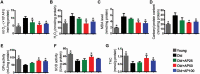
Skeletal muscle atrophy in the aged causes loss in muscle mass and functions. Naturally occurring antioxidant flavonoid apigenin is able to ameliorate obesity- and denervation-induced muscle atrophies, but its effects on age-related muscle atrophy remain unknown. We hypothesized that apigenin can relieve muscle atrophy in aged mice, probably through special effects on reactive oxygen species and enzymes with antioxidant functions. For the male mice of the study, apigenin showed significant dose-dependent effects in relieving aging-related muscle atrophy according to results of frailty index as indicator of frailty associated with aging, grip strength, and running distance. Apigenin also improved myofiber size and morphological features and increased mitochondria number and volume, as manifested by succinate dehydrogenase staining and transmission electron microscopy. Our tests also suggested that apigenin promoted activities of enzymes such as superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase for antioxidation and those for aerobic respiration such as mitochondrial respiratory enzyme complexes I, II, and IV, increased ATP, and enhanced expression of genes such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator 1α, mitochondrial transcription factor A, nuclear respiratory factor-1, and ATP5B involved in mitochondrial biogenesis. The data also suggested that apigenin inhibited Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kD-interacting protein 3 and DNA fragmentation as indicators of mitophagy and apoptosis in aged mice with skeletal muscle atrophy. Together, the results suggest that apigenin relieves age-related skeletal muscle atrophy through reducing oxidative stress and inhibiting hyperactive autophagy and apoptosis.
Keywords: Apigenin; Apoptosis; Mitophagy; Reactive oxygen species; Skeletal muscle atrophy.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Gerontological Society of America.
Figures
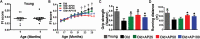
Similar articles
-
Astaxanthin Prevents Atrophy in Slow Muscle Fibers by Inhibiting Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species via a Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis Pathway.Nutrients. 2021 Jan 26;13(2):379. doi: 10.3390/nu13020379. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 33530505 Free PMC article.
-
Tanshinone IIA alleviates inflammation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy by regulating mitochondrial dysfunction.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024 Dec;762:110215. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2024.110215. Epub 2024 Nov 14. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 39547552
-
Mitophagy regulates mitochondrial network signaling, oxidative stress, and apoptosis during myoblast differentiation.Autophagy. 2019 Sep;15(9):1606-1619. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1591672. Epub 2019 Apr 7. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30859901 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Exercise and TFAM in Preventing Skeletal Muscle Atrophy.J Cell Physiol. 2017 Sep;232(9):2348-2358. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25737. Epub 2017 Apr 12. J Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27966783 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial health and muscle plasticity after spinal cord injury.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019 Feb;119(2):315-331. doi: 10.1007/s00421-018-4039-0. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30539302 Review.
Cited by
-
Restorative effects of (+)-epicatechin in a rodent model of aging induced muscle atrophy: underlying mechanisms.Food Funct. 2024 Apr 2;15(7):3669-3679. doi: 10.1039/d3fo04004f. Food Funct. 2024. PMID: 38487922 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative balance score is inversely associated with low muscle mass in young and middle-aged adults: a cross-sectional NHANES study.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025 Apr 22;26(1):398. doi: 10.1186/s12891-025-08459-5. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2025. PMID: 40264077 Free PMC article.
-
Accounting Gut Microbiota as the Mediator of Beneficial Effects of Dietary (Poly)phenols on Skeletal Muscle in Aging.Nutrients. 2023 May 18;15(10):2367. doi: 10.3390/nu15102367. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37242251 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apigenin attenuates LPS-induced neurotoxicity and cognitive impairment in mice via promoting mitochondrial fusion/mitophagy: role of SIRT3/PINK1/Parkin pathway.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Dec;239(12):3903-3917. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06262-x. Epub 2022 Oct 26. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 36287214 Free PMC article.
-
Phytoecdysteroids and Anabolic Effect of Atriplex dimorphostegia: UPLC-PDA-MS/MS Profiling, In Silico and In Vivo Models.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 3;12(1):206. doi: 10.3390/plants12010206. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36616335 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

