Prognostic value of copeptin in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32857795
- PMCID: PMC7454979
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0238288
Prognostic value of copeptin in patients with acute coronary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to evaluate the value of copeptin in predicting mortality including both short-term and long-term mortality in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS).
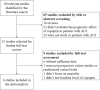
Methods: Potential studies were searched and selected through PubMed, Embase and Cochrane databases up to December 2019. The predictive performance was evaluated by the pooled sensitivity and specificity, and summary receiver operating characteristic curves. Cochran's Q test and I2 index were used to assess between-study heterogeneity, and Deek's test and funnel plots were used to assess publication bias.
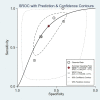
Results: Total six studies comprising 2269 patients were included in this meta-analysis. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve of copeptin in predicting mortality in patients with ACS was 0.73 (95% CI: 0.69-0.77). The pooled sensitivity and specificity of copeptin were 0.77 (95% CI: 0.59-0.89) and 0.60 (95% CI: 0.47-0.71), respectively. Significant between-study heterogeneity was identified in both sensitivity (P = 0.01; I2 = 69.76%) and specificity (P<0.001; I2 = 97.32%) among the six included studies. The meta-regression analysis indicated that the number of study centers was significantly associated with the heterogeneity of sensitivity (P = 0.03), whereas the study design (P = 0.03) and duration of follow-up (P<0.001) were significantly associated with the heterogeneity of specificity.
Conclusions: Copeptin has acceptable prognostic value for mortality in patients with ACS. Further studies based on multimarker strategy are needed to evaluate the prognostic value of copeptin for ACS in conjunction with other well-established biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Copeptin in heart failure: Review and meta-analysis.Clin Chim Acta. 2017 Dec;475:36-43. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2017.10.001. Epub 2017 Oct 2. Clin Chim Acta. 2017. PMID: 28982590 Review.
-
Copeptin as a Prognostic Marker in Acute Chest Pain and Suspected Acute Coronary Syndrome.Dis Markers. 2018 Jan 24;2018:6597387. doi: 10.1155/2018/6597387. eCollection 2018. Dis Markers. 2018. PMID: 29619130 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
[Meta-analysis on the diagnostic value of laser Doppler imaging for burn depth].Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017 May 20;33(5):301-308. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-2587.2017.05.009. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi. 2017. PMID: 28651422 Chinese.
-
Role of copeptin in dual-cardiac marker strategy for patients with chest pain presented to ED.Am J Emerg Med. 2015 Dec;33(12):1732-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.08.011. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Am J Emerg Med. 2015. PMID: 26341809 Clinical Trial.
-
The diagnosis and prognostic value of plasma copeptin in traumatic brain injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Neurol Sci. 2021 Feb;42(2):539-551. doi: 10.1007/s10072-020-05019-8. Epub 2021 Jan 3. Neurol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33389249
Cited by
-
Critical appraisal of the 2020 ESC guideline recommendations on diagnosis and risk assessment in patients with suspected non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome.Clin Res Cardiol. 2021 Sep;110(9):1353-1368. doi: 10.1007/s00392-021-01821-2. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Clin Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33635437 Free PMC article.
-
Copeptin and the prognosis of patients with coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis.Ir J Med Sci. 2023 Oct;192(5):2129-2141. doi: 10.1007/s11845-023-03276-y. Epub 2023 Jan 31. Ir J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 36719516
-
Performance of Copeptin for Early Diagnosis of Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of 14,139 Patients.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021 Dec 27;9(1):6. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9010006. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2021. PMID: 35050216 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic value of elabela peptide on predicting major adverse cardiac events of NSTEMI patients in emergency department.Ir J Med Sci. 2025 Aug 14. doi: 10.1007/s11845-025-04054-8. Online ahead of print. Ir J Med Sci. 2025. PMID: 40810830
-
Copeptin in Acute Myocardial Infarction: Is There a Role in the Era of High-Sensitivity Troponins?J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025 Apr 9;12(4):144. doi: 10.3390/jcdd12040144. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2025. PMID: 40278203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang Q, Zhang RY, Qiu JP, Zhang JF, Wang XL, Jiang L, et al. One-year clinical outcome of interventionalist- versus patient-transfer strategies for primary percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: results from the REVERSE-STEMI study. Circulation Cardiovascular quality and outcomes. 2011;4(3):355–62. 10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.110.958785 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Thygesen K, Mair J, Mueller C, Huber K, Weber M, Plebani M, et al. Recommendations for the use of natriuretic peptides in acute cardiac care: a position statement from the Study Group on Biomarkers in Cardiology of the ESC Working Group on Acute Cardiac Care. European heart journal. 2012;33(16):2001–6. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehq509 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

